Atorvastatin prevents glomerular extracellular matrix formation by interfering with the PKC signaling pathway
- PMID: 29532876
- PMCID: PMC5928626
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8724
Atorvastatin prevents glomerular extracellular matrix formation by interfering with the PKC signaling pathway
Abstract
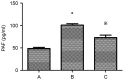
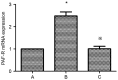
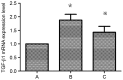
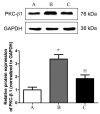
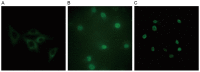
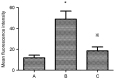
Platelet-activating factor (PAF) promotes glomerular extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition, primarily through activation of the protein kinase C (PKC) pathway. The present study was designed to investigate whether atorvastatin, which mediates a protective effect against glomerular ECM deposition and diabetic neuropathy, may interfere with the PKC‑transforming growth factor‑β1 (TGF‑β1) pathway in a model of human mesangial cells (HMCs) exposed to a high glucose (HG) and lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) environment. HMCs were divided into three treatment groups: Control, high glucose and lysophosphatidylcholine (HG+LPC), and HG+LPC+atorvastatin. Cells were cultured for 24 h. The levels of the ECM‑associated molecules collagen IV (Col IV) and fibronectin (Fn) in the supernatant were detected using an ELISA kit. PKC‑β1, TGF‑β1 and PAF‑receptor gene expression was detected by reverse transcription‑quantitative polymerase chain reaction. PKC‑β1 and TGF‑β1 protein expression was detected by western blotting, and the subcellular localization of PKC‑β1 was assessed using immunofluorescence. The results indicated that atorvastatin may reduce the secretion of ECM components (Fn and Col IV) in HMCs in a HG and LPC environment, by inhibiting the increase in PAF secretion and the activation of the PKC‑TGF‑β1 signaling pathway.
Keywords: platelet-activating factor; high glucose and lysophosphatidylcholine; protein kinase C; extracellular matrix; atorvastatin.
Figures




References
-
- Fragopoulou E, Iatrou C, Antonopoulou S, Ruan XZ, Fernando RL, Powis SH, Moorhead JF, Varghese Z. Platelet-activating factor (PAF) increase intracellular lipid accumulation by increasing both LDL and scavenger receptors in human mesangial cells. J Lab Clin Med. 2006;147:281–289. doi: 10.1016/j.lab.2006.01.004. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

