MicroRNA-214-5p/TGF-β/Smad2 signaling alters adipogenic differentiation of bone marrow stem cells in postmenopausal osteoporosis
- PMID: 29532880
- PMCID: PMC5928609
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8713
MicroRNA-214-5p/TGF-β/Smad2 signaling alters adipogenic differentiation of bone marrow stem cells in postmenopausal osteoporosis
Abstract
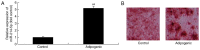
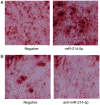
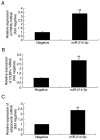
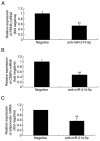
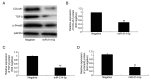
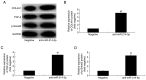
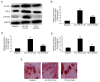
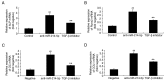
Postmenopausal osteoporosis (OPM) is a common type of osteoporosis in females. It is a systemic, chronic bone disease that presents as microstructure degradation of osseous tissue, decreased bone mineral density and increased osteopsathyrosis caused by hypoovarianism and reduced estrogen levels in the body following menopause. In the present study, the role of microRNA (miR)‑214‑5p in the regulation of the expression of bone marrow stem cells (BMSCs) was investigated, and its molecular mechanism of osteogenic induction in vitro was assessed. When dexamethasone‑induced adipogenic differentiation was performed, miR‑214‑5p expression was increased compared with the control group, as determined by RT‑qPCR. Furthermore, oil red O staining, RT‑qPCR and western blot analysis demonstrated that overexpression of miR‑214‑5p promoted adipogenic differentiation, inhibited alkaline phosphatase (ALP), runt‑related transcription factor 2 (Runx2), osteocalcin (OC) and collagen α‑1 (I) chain (COL1A1) mRNA expression, and suppressed transforming growth factor (TGF)‑β, phosphorylated (p)‑Smad2 and collagen type IV α1 chain (COL4A1) protein expression in BMSCs. Additionally, downregulation of miR‑214‑5p increased the ALP, Runx2, OC and COL1 mRNA expression and increased TGF‑β, Smad2 and COL4A1 protein expression in BMSCs. Furthermore, a TGF‑β inhibitor was employed to inhibit TGF‑β expression in BMSCs following miR‑214‑5p downregulation, which led to reduced Smad2, TGF‑β and COL4A1 protein expression, and ALP, Runx2, OC and COL1 mRNA expression was also reduced, compared with the miR‑214‑5p downregulation only group. It was demonstrated that miR‑214‑5p may weaken osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs through regulating COL4A1. In conclusion, the results of the present study indicated that miR‑214‑5p may promote the adipogenic differentiation of BMSCs through regulation of the TGF‑β/Smad2/COL4A1 signaling pathway, and potentially may be used to develop a novel drug for postmenopausal osteoporosis.
Keywords: microRNA-214-5p; adipogenic differentiation; bone marrow stem cells; transforming growth factor-β; Smad2.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MiR-210 promotes bone formation in ovariectomized rats by regulating osteogenic/adipogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through downregulation of EPHA2.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Oct 30;18(1):811. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-04213-6. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 37904187 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of GGCX on the differentiation function of osteoporosis bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through regulating TGFβ/smad signaling pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Sep;23(17):7224-7231. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201909_18825. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31539109
-
Tanshinone IIA promotes osteogenic differentiation potential and suppresses adipogenic differentiation potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.Mol Med Rep. 2024 Oct;30(4):177. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13301. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 39129299 Free PMC article.
-
Mangiferin promotes the osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells via TGF‑β/SMAD2 signaling.Mol Med Rep. 2022 Aug;26(2):266. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12782. Epub 2022 Jun 28. Mol Med Rep. 2022. PMID: 35762316
-
Physical Activity and Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Aging Decay: Modulation of Pathways in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Jun 6;58(6):767. doi: 10.3390/medicina58060767. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35744030 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
microRNA-214-3p Suppresses Ankylosing Spondylitis Fibroblast Osteogenesis via BMP-TGFβ Axis and BMP2.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Apr 15;11:609753. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.609753. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33935961 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Micro RNA and Long-Non-Coding RNA in Osteoporosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 10;21(14):4886. doi: 10.3390/ijms21144886. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32664424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs and long noncoding RNAs: new regulators in cell fate determination of mesenchymal stem cells.RSC Adv. 2019 Nov 14;9(64):37300-37311. doi: 10.1039/c9ra06563f. eCollection 2019 Nov 13. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35542270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone marrow adiposity during pathologic bone loss: molecular mechanisms underlying the cellular events.J Mol Med (Berl). 2022 Feb;100(2):167-183. doi: 10.1007/s00109-021-02164-1. Epub 2021 Nov 9. J Mol Med (Berl). 2022. PMID: 34751809 Review.
-
miR-214-5p Regulating Differentiation of Intramuscular Preadipocytes in Goats via Targeting KLF12.Front Genet. 2021 Dec 22;12:748629. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.748629. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 35003206 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pawlowski JW, Martin BR, McCabe GP, McCabe L, Jackson GS, Peacock M, Barnes S, Weaver CM. Impact of equol-producing capacity and soy-isoflavone profiles of supplements on bone calcium retention in postmenopausal women: A randomized crossover trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2015;102:695–703. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.114.093906. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Itabashi A, Yoh K, Chines AA, Miki T, Takada M, Sato H, Gorai I, Sugimoto T, Mizunuma H, Ochi H, et al. Bridging analysis of the efficacy and safety of bazedoxifene in Japanese and global populations of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Metab. 2015;33:61–72. doi: 10.1007/s00774-013-0554-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Filip R, Possemiers S, Heyerick A, Pinheiro I, Raszewski G, Davicco MJ, Coxam V. Twelve-month consumption of a polyphenol extract from olive (Olea europaea) in a double blind, randomized trial increases serum total osteocalcin levels and improves serum lipid profiles in postmenopausal women with osteopenia. J Nutr Health Aging. 2015;19:77–86. doi: 10.1007/s12603-014-0480-x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

