DIALS: implementation and evaluation of a new integration package
- PMID: 29533234
- PMCID: PMC5947772
- DOI: 10.1107/S2059798317017235
DIALS: implementation and evaluation of a new integration package
Abstract
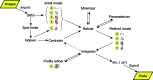
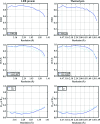
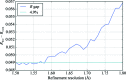
The DIALS project is a collaboration between Diamond Light Source, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and CCP4 to develop a new software suite for the analysis of crystallographic X-ray diffraction data, initially encompassing spot finding, indexing, refinement and integration. The design, core algorithms and structure of the software are introduced, alongside results from the analysis of data from biological and chemical crystallography experiments.
Keywords: DIALS; X-ray diffraction; data processing; methods development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Improving signal strength in serial crystallography with DIALS geometry refinement.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2018 Sep 1;74(Pt 9):877-894. doi: 10.1107/S2059798318009191. Epub 2018 Sep 3. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2018. PMID: 30198898 Free PMC article.
-
Electron diffraction data processing with DIALS.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2018 Jun 1;74(Pt 6):506-518. doi: 10.1107/S2059798318007726. Epub 2018 May 30. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2018. PMID: 29872002 Free PMC article.
-
Processing serial synchrotron crystallography diffraction data with DIALS.Methods Enzymol. 2024;709:207-244. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2024.10.004. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Methods Enzymol. 2024. PMID: 39608945
-
X-ray data processing.Biosci Rep. 2017 Oct 6;37(5):BSR20170227. doi: 10.1042/BSR20170227. Print 2017 Oct 31. Biosci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28899925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ongoing developments in CCP4 for high-throughput structure determination.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2002 Nov;58(Pt 11):1929-36. doi: 10.1107/s0907444902016116. Epub 2002 Oct 21. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2002. PMID: 12393924 Review.
Cited by
-
GPC3-Unc5 receptor complex structure and role in cell migration.Cell. 2022 Oct 13;185(21):3931-3949.e26. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.09.025. Cell. 2022. PMID: 36240740 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing pathological imperfections in macromolecular crystals: lattice disorders and modulations.Crystallogr Rev. 2020;26(1):3-50. doi: 10.1080/0889311x.2019.1692341. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Crystallogr Rev. 2020. PMID: 33041501 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A 2.8 Å Structure of Zoliflodacin in a DNA Cleavage Complex with Staphylococcus aureus DNA Gyrase.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 13;24(2):1634. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021634. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675148 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational heterogeneity in apo and drug-bound structures of Toxoplasma gondii prolyl-tRNA synthetase.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2019 Nov 1;75(Pt 11):714-724. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X19014808. Epub 2019 Nov 7. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2019. PMID: 31702585 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation of an unusual cysteine pair in the Rieske carnitine monooxygenase CntA catalytic site.FEBS J. 2023 Jun;290(11):2939-2953. doi: 10.1111/febs.16722. Epub 2023 Jan 19. FEBS J. 2023. PMID: 36617384 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrahams, D. & Grosse-Kunstleve, R. W. (2003). C/C++ Users J. 21, 29–36.
-
- Adams, P. D. et al. (2010). Acta Cryst. D66, 213–221. - PubMed
-
- Brewster, A. S., Waterman, D. G., Parkhurst, J. M., Gildea, R. J., Michels-Clark, T., Young, I. D., Bernstein, H. J., Winter, G., Evans, G. & Sauter, N. K. (2016). Comput. Crystallogr. Newsl. 7, 32–53. https://www.phenix-online.org/newsletter/CCN_2016_07.pdf.
-
- Bricogne, G. (1986a). Proceedings of the EEC Cooperative Workshop on Position-Sensitive Detector Software (Phases I and II). Paris: LURE.
-
- Bricogne, G. (1986b). Proceedings of the EEC Cooperative Workshop on Position-Sensitive Detector Software (Phase III). Paris: LURE.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 202933/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 283570/Seventh Framework Programme, FP7 Research Infrastructures/International
- R01 GM095887/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM117126/National Institutes of Health, National Institute of General Medical Sciences/International
- GM095887/National Institutes of Health, National Institute of General Medical Sciences/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

