Long-Term Increase of Radiographic Damage and Disability in Patients with RA in Relation to Disease Duration in the Era of Biologics. Results from the SCQM Cohort
- PMID: 29533997
- PMCID: PMC5867583
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm7030057
Long-Term Increase of Radiographic Damage and Disability in Patients with RA in Relation to Disease Duration in the Era of Biologics. Results from the SCQM Cohort
Abstract
Objectives: There is little information on the relation between disease duration, disability and radiographic outcome since the introduction of biologics into the therapy of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). No long -term cohort studies have been conducted on this subject so far. To analyse radiographic damage, disability, and disease activity in RA-patients dependent on disease duration in the Swiss national RA cohort (SCQM).
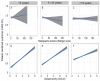
Methods: The primary outcome was the association between the radiographic destruction, assessed by Ratingen scores, and disease duration. All patients with at least one clinical visit were analysed with polynomial and multiple negative binomial models.
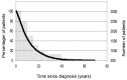
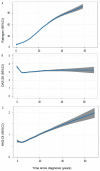
Results: The disease duration in the 8678 patients with available radiographs analysed ranged between less than 1 and more than 65 years (median 8.3). Disease duration and radiographic destruction were significantly associated with an average increase of Ratingen scores by 8.3% per year. Apart from disease duration, positive rheumatoid factor was the strongest predictor for radiographic destruction. While DAS28-scores remained stable in patients with a disease duration of more than 5 years (median DAS28 2.8), HAQ-DI scores increased continuously by 0.018 for each additional year.
Conclusion: In this RA cohort, patients show a continuous increase of articular destruction and physical disability in parallel with disease duration. Even when nowadays a satisfactory control of disease activity can be achieved in most patients, RA remains a destructive disease leading to joint destruction and physical disability in many patients.
Keywords: ACPA; DAS28; HAQ-DI; Ratingen score; disease duration; radiographic destruction; rheumatoid arthritis; rheumatoid factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose that directly or indirectly might affect, or be perceived to affect, the conduct or reporting of the work they have submitted.
Figures

References
-
- Wolfe F., Hawley D.J. The longterm outcomes of rheumatoid arthritis: Work disability: A prospective 18 year study of 823 patients. J. Rheumatol. 1998;25:2108–2117. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

