Clinical usefulness of the SAMe-TT2R2 score: A systematic review and simulation meta-analysis
- PMID: 29534092
- PMCID: PMC5849337
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194208
Clinical usefulness of the SAMe-TT2R2 score: A systematic review and simulation meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) therapy is safer and more effective when patients have a high time within the therapeutic range and low international normalised ratio variability. The SAMe-TT2R2 score aims to identify those at risk for poor VKA control.
Objectives: To evaluate the predictive value and clinical usefulness of the SAMe-TT2R2 score to identify those at risk for poor VKA control.
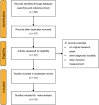
Methods: We performed a systematic review in MEDLINE and Embase for original research papers assessing the SAMe-TT2R2's relation to poor TTR. We performed a meta-analysis where scores ≥ 2 and ≥ 3 predicting TTR < 70%. When studies evaluated other cutoffs for TTR or SAMe-TT2R2, they were harmonised by multiple simulations with patient characteristics from the individual studies, if the data were available.
Results: 16 studies were identified and used in the meta-analysis: 4 and 2 times directly, 8 and 8 times harmonised for scores ≥ 2 and ≥ 3, respectively (not all studies provided information about both cutoffs). The sensitivities and specificities were too heterogeneous to pool. The positive likelihood ratios were 1.25 (1.14-1.38) for a score ≥ 2, and 1.24 (1.09-1.40) for a score ≥ 3; the negative ones were 0.87 (0.82-0.93) and 0.96 (0.91-1.02), respectively. This shows that the post-test probabilities hardly differ from the prior probability (prevalence).
Conclusion: The SAMe-TT2R2 score does predict low TTR, but the effect is small. Its effect on individual patients is too limited to be clinically useful.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Kirchhof P, Benussi S, Kotecha D, Ahlsson A, Atar D, Casadei B, et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur Heart J. 2016;37(38):2893–2962. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw210 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Björck F, Renlund H, Lip GYH, Wester P, Svensson PJ, Själander A. Outcomes in a Warfarin-Treated Population With Atrial Fibrillation. JAMA Cardiol. 2016;1(2):172 doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2016.0199 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sandén P, Renlund H, Svensson PJ, Själander A. Bleeding complications and mortality in warfarin-treated VTE patients, dependence of INR variability and iTTR. Thromb Haemost. 2016;117(1):27–32. doi: 10.1160/TH16-06-0489 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Veeger NJGM, Piersma-Wichers M, Hillege HL, Crijns HJGM, van der Meer J. Early detection of patients with a poor response to vitamin K antagonists: the clinical impact of individual time within target range in patients with heart disease. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4(7):1625–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2006.01997.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- ROSE AJ, Hylek EM, Ozonoff A, Ash AS, REISMAN JI, BERLOWITZ DR. Patient characteristics associated with oral anticoagulation control: results of the Veterans AffaiRs Study to Improve Anticoagulation (VARIA). J Thromb Haemost. 2010;8(10):2182–2191. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.03996.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

