New elephant crisis in Asia-Early warning signs from Myanmar
- PMID: 29534096
- PMCID: PMC5849331
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194113
New elephant crisis in Asia-Early warning signs from Myanmar
Abstract
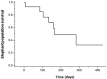
In the southern Bago Yoma mountain range in Myanmar, Asian elephants are being killed at a disturbing rate. This emerging crisis was identified initially through a telemetry study when 7 of 19 of collared elephants were poached within a year of being fitted with a satellite-GPS collar. Subsequent follow up of ground teams confirmed the human caused death or disappearance of at least 19 elephants, including the seven collared individuals, within a 35 km2 area in less than two years. The carcasses of 40 additional elephants were found in areas located across south-central Myanmar once systematic surveys began by our team and collaborators. In addition to the extreme rate of loss, this study documents the targeting of elephants for their skin instead of the more common ivory, an increasing trend in Myanmar. Intensive research programs focused on other conservation problems identified this issue and are now encouraging local authorities to prioritize anti-poaching efforts and improve conservation policies within the country. Myanmar represents one of the last remaining countries in Asia with substantial wildlands suitable for elephants. Increasing rates of human-elephant conflict and poaching events in this country pose a dire threat to the global population.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Maisels F, Strindberg S, Blake S, Wittemyer G, Hart J, Williamson EA, et al. Devastating Decline of Forest Elephants in Central Africa. Kolokotronis S-O, editor. PLoS One. 2013. March 4;8(3):e59469 Available from: http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059469 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Underwood FM, Burn RW, Milliken T. Dissecting the Illegal Ivory Trade: An Analysis of Ivory Seizures Data. Montoya ARH, editor. PLoS One. 2013;8(10):e76539 Available from: http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0076539 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gao Y, Clark SG. Elephant ivory trade in China: Trends and drivers. Biol Conserv. 2014;180:23–30. Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006320714003371
-
- Wittemyer G, Northrup JM, Blanc J, Douglas-Hamilton I, Omondi P, Burnham KP. Illegal killing for ivory drives global decline in African elephants. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014;111(36):13117–21. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25136107 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kideghesho JR. The Elephant poaching crisis in Tanzania: a need to reverse the trend and the way forward. Trop Conserv Sci. 2016;9(91):369–88. Available from: doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1400103 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

