Genetic variants in the LAMA5 gene in pediatric nephrotic syndrome
- PMID: 29534211
- PMCID: PMC6399483
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfy028
Genetic variants in the LAMA5 gene in pediatric nephrotic syndrome
Abstract
Background: Nephrotic syndrome (NS), a chronic kidney disease, is characterized by significant loss of protein in the urine causing hypoalbuminemia and edema. In general, ∼15% of childhood-onset cases do not respond to steroid therapy and are classified as steroid-resistant NS (SRNS). In ∼30% of cases with SRNS, a causative mutation can be detected in one of 44 monogenic SRNS genes. The gene LAMA5 encodes laminin-α5, an essential component of the glomerular basement membrane. Mice with a hypomorphic mutation in the orthologous gene Lama5 develop proteinuria and hematuria.
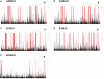
Methods: To identify additional monogenic causes of NS, we performed whole exome sequencing in 300 families with pediatric NS. In consanguineous families we applied homozygosity mapping to identify genomic candidate loci for the underlying recessive mutation.
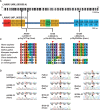
Results: In three families, in whom mutations in known NS genes were excluded, but in whom a recessive, monogenic cause of NS was strongly suspected based on pedigree information, we identified homozygous variants of unknown significance (VUS) in the gene LAMA5. While all affected individuals had nonsyndromic NS with an early onset of disease, their clinical outcome and response to immunosuppressive therapy differed notably.
Conclusion: We here identify recessive VUS in the gene LAMA5 in patients with partially treatment-responsive NS. More data will be needed to determine the impact of these VUS in disease management. However, familial occurrence of disease, data from genetic mapping and a mouse model that recapitulates the NS phenotypes suggest that these genetic variants may be inherited factors that contribute to the development of NS in pediatric patients.
Keywords: genetic variants; inherited diseases; nephrotic syndrome; treatment response in pediatric nephrotic syndrome; whole exome sequencing.
© The Author(s) 2018. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Kim JS, Bellew CA, Silverstein DM. et al. High incidence of initial and late steroid resistance in childhood nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int 2005; 68: 1275–1281 - PubMed
-
- Ehrich JH, Geerlings C, Zivicnjak M. et al. Steroid-resistant idiopathic childhood nephrosis: overdiagnosed and undertreated. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2007; 22: 2183–2193 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

