Impact of Interferon Lambda 4 Genotype on Interferon-Stimulated Gene Expression During Direct-Acting Antiviral Therapy for Hepatitis C
- PMID: 29534310
- PMCID: PMC6207923
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.29877
Impact of Interferon Lambda 4 Genotype on Interferon-Stimulated Gene Expression During Direct-Acting Antiviral Therapy for Hepatitis C
Abstract
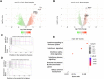
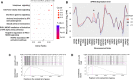
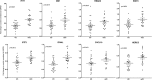
New directly acting antivirals (DAAs) provide very high cure rates in most patients infected by hepatitis C virus (HCV). However, some patient groups have been relatively harder to treat, including those with cirrhosis or infected with HCV genotype 3. In the recent BOSON trial, genotype 3, patients with cirrhosis receiving a 16-week course of sofosbuvir and ribavirin had a sustained virological response (SVR) rate of around 50%. In patients with cirrhosis, interferon lambda 4 (IFNL4) CC genotype was significantly associated with SVR. This genotype was also associated with a lower interferon-stimulated gene (ISG) signature in peripheral blood and in liver at baseline. Unexpectedly, patients with the CC genotype showed a dynamic increase in ISG expression between weeks 4 and 16 of DAA therapy, whereas the reverse was true for non-CC patients. Conclusion: These data provide an important dynamic link between host genotype and phenotype in HCV therapy also potentially relevant to naturally acquired infection. (Hepatology 2018; 00:000-000).
© 2018 The Authors. Hepatology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures




References
-
- Heim MH, Bochud P‐Y, George J. Host‐hepatitis C viral interactions: the role of genetics. J Hepatol 2016;65:S22‐S32. - PubMed
-
- Lauer G, Walker B. Hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med 2001;345:41‐52. - PubMed
-
- Fried MW, Shiffman ML, Reddy KR, Smith C, Marinos G, Goncales L, Jr. , et al. PEG‐interferon alfa‐2A plus ribarivin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med 2002;347:975‐982. - PubMed
-
- Zeuzem S, Andreone P, Pol S, Lawitz E, Diago M, Roberts S, et al. Telaprevir for retreatment of HCV infection. N Engl J Med 2011;364:2417‐2428. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 090532/Z/09/Z/Wellcome Trust Fund/International
- U19AI082630/GF/NIH HHS/United States
- RP-2016-07-012/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- EME/14/02/17/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- WT109965MA/Wellcome Trust Fund/International
- U19 AI082630/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI082630/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K01532X/1/Medical Research Council (MRC)/International
- MR/K01532X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- NIHR Biomedical Research Centre/International
- NIHR Senior Fellowship/International
- 109965/Z/15/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

