Assessment of Mycotoxin Exposure in Breastfeeding Mothers with Celiac Disease
- PMID: 29534461
- PMCID: PMC5872754
- DOI: 10.3390/nu10030336
Assessment of Mycotoxin Exposure in Breastfeeding Mothers with Celiac Disease
Abstract
Objective: To assess the risk of mycotoxin exposure (aflatoxin M1, ochratoxin A, and zearalenone) in celiac disease (CD) breastfeeding mothers and healthy control mothers, as well as in their offspring, by quantifying these contaminants in breast milk.
Study design: Thirty-five breastfeeding women with CD on a gluten-free diet and 30 healthy breastfeeding controls were recruited. Milk sampling was performed three times per day for three consecutive days. Mycotoxin content was investigated by an analytical method using immunoaffinity column clean-up and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with fluorometric detection.
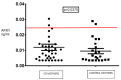
Results: Aflatoxin M1 (AFM1) was detected in 37% of CD group samples (mean ± SD = 0.012 ± 0.011 ng/mL; range = 0.003-0.340 ng/mL). The control group showed lower mean AFM1 concentration levels in 24% of the analyzed samples (0.009 ± 0.007 ng/mL; range = 0.003-0.067 ng/mL, ANOVA on ranks, p-value < 0.01). Ochratoxin A and zearalenone did not differ in both groups.
Conclusion: Breast milk AFM1 contamination for both groups is lower than the European safety threshold. However, the estimated exposures of infants from CD mothers and control mothers was much higher (≃15 times and ≃11 times, respectively) than the threshold set by the joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA). Since incongruities exist between JECFA and the European Union standard, a novel regulatory review of the available data on this topic is desirable. Protecting babies from a neglected risk of high AFM1 exposure requires prompt regulatory and food-control policies.
Keywords: breast milk; celiac disease; mycotoxins.
Conflict of interest statement
C.C. receives a consultancy honorary from Schär and Menarini Diagnostics. The other authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this article to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An assessment of the occurrence and nutritional factors associated with aflatoxin M1, ochratoxin A, and zearalenone in the breast milk of nursing mothers in Hamadan, Iran.Toxicon. 2020 Nov;187:209-213. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2020.09.011. Epub 2020 Sep 22. Toxicon. 2020. PMID: 32971098
-
Co-occurrence of mycotoxins in commercial formula milk and cereal-based baby food on the Qatar market.Food Addit Contam Part B Surveill. 2018 Sep;11(3):191-197. doi: 10.1080/19393210.2018.1437785. Epub 2018 May 15. Food Addit Contam Part B Surveill. 2018. PMID: 29490584
-
Occurrence of aflatoxin M1 in human breast milk in Bangladesh.Mycotoxin Res. 2021 Aug;37(3):241-248. doi: 10.1007/s12550-021-00436-w. Epub 2021 Jun 22. Mycotoxin Res. 2021. PMID: 34159478
-
Evaluation of Mycotoxins in Infant Breast Milk and Infant Food, Reviewing the Literature Data.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Jul 30;13(8):535. doi: 10.3390/toxins13080535. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34437408 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary exposure assessment to mycotoxins through total diet studies. A review.Food Chem Toxicol. 2019 Jun;128:8-20. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2019.03.033. Epub 2019 Mar 23. Food Chem Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30910684 Review.
Cited by
-
Detection of multimycotoxins in camel feed and milk samples and their comparison with the levels in cow milk.Food Sci Nutr. 2021 Dec 13;10(2):609-616. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2677. eCollection 2022 Feb. Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 35154696 Free PMC article.
-
Occurrence of Aflatoxin M1 in Raw Milk Marketed in Italy: Exposure Assessment and Risk Characterization.Front Microbiol. 2019 Nov 8;10:2516. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02516. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31787941 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal follow-up of zearalenone and deoxynivalenol mycotoxins in breast milk in the first five months of life.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2023 May 30;24(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s40360-023-00677-8. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37254214 Free PMC article.
-
Aspergillus flavus and Fusarium verticillioides Interaction: Modeling the Impact on Mycotoxin Production.Front Microbiol. 2019 Nov 12;10:2653. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02653. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31781087 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge and Behavioral Habits to Reduce Mycotoxin Dietary Exposure at Household Level in a Cohort of German University Students.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Oct 26;13(11):760. doi: 10.3390/toxins13110760. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34822544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Some Naturally Occurring Substances: Food Items and Constituents, Heterocyclic Aromatic Amines and Mycotoxins. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. [(accessed on 12 December 2017)];1996 Volume 56 Available online: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Monographs/vol56/mono56.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

