Diabetes Mellitus and Ischemic Heart Disease: The Role of Ion Channels
- PMID: 29534462
- PMCID: PMC5877663
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19030802
Diabetes Mellitus and Ischemic Heart Disease: The Role of Ion Channels
Abstract
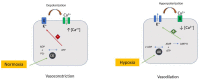
Diabetes mellitus is one the strongest risk factors for cardiovascular disease and, in particular, for ischemic heart disease (IHD). The pathophysiology of myocardial ischemia in diabetic patients is complex and not fully understood: some diabetic patients have mainly coronary stenosis obstructing blood flow to the myocardium; others present with coronary microvascular disease with an absence of plaques in the epicardial vessels. Ion channels acting in the cross-talk between the myocardial energy state and coronary blood flow may play a role in the pathophysiology of IHD in diabetic patients. In particular, some genetic variants for ATP-dependent potassium channels seem to be involved in the determinism of IHD.
Keywords: coronary blood flow; diabetes mellitus; ion channels; ischemic heart disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization . Global Report on Diabetes. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

