Research on Flow Field Perception Based on Artificial Lateral Line Sensor System
- PMID: 29534499
- PMCID: PMC5877381
- DOI: 10.3390/s18030838
Research on Flow Field Perception Based on Artificial Lateral Line Sensor System
Abstract
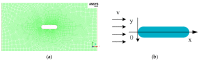
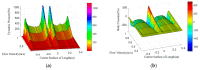
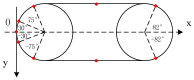
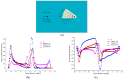
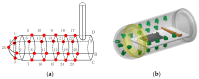
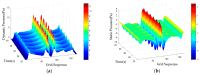
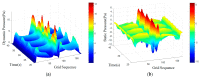
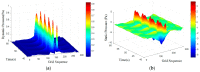
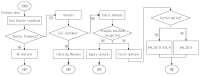
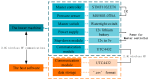
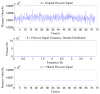
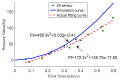
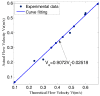
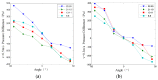
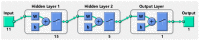
In nature, the lateral line of fish is a peculiar and important organ for sensing the surrounding hydrodynamic environment, preying, escaping from predators and schooling. In this paper, by imitating the mechanism of fish lateral canal neuromasts, we developed an artificial lateral line system composed of micro-pressure sensors. Through hydrodynamic simulations, an optimized sensor structure was obtained and the pressure distribution models of the lateral surface were established in uniform flow and turbulent flow. Carrying out the corresponding underwater experiment, the validity of the numerical simulation method is verified by the comparison between the experimental data and the simulation results. In addition, a variety of effective research methods are proposed and validated for the flow velocity estimation and attitude perception in turbulent flow, respectively and the shape recognition of obstacles is realized by the neural network algorithm.
Keywords: artificial lateral line system; flow field perception; hydrodynamic simulation; neural network; velocity estimation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



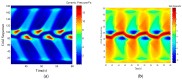
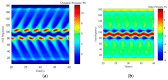


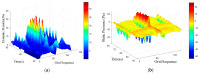
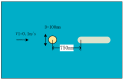





References
-
- Blaxter J.H.S., Fuiman L.A. In: The Mechanosensory Lateral Line: Neurobiology and Evolution. Coombs S., Gorner P., Munz H., editors. Springer Science & Business Media; Berlin, German: 2012. pp. 481–499.
-
- Hoekstra D., Janssen J. Non-visual feeding behavior of the mottled sculpin, Cottus bairdi, in Lake Michigan Environ. Biol. Fishes. 2006;12:111–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00002763. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

