Vitamin A bio-modulates apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway after hypoxic-ischemic brain damage
- PMID: 29534734
- PMCID: PMC5851324
- DOI: 10.1186/s13041-018-0360-0
Vitamin A bio-modulates apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway after hypoxic-ischemic brain damage
Abstract
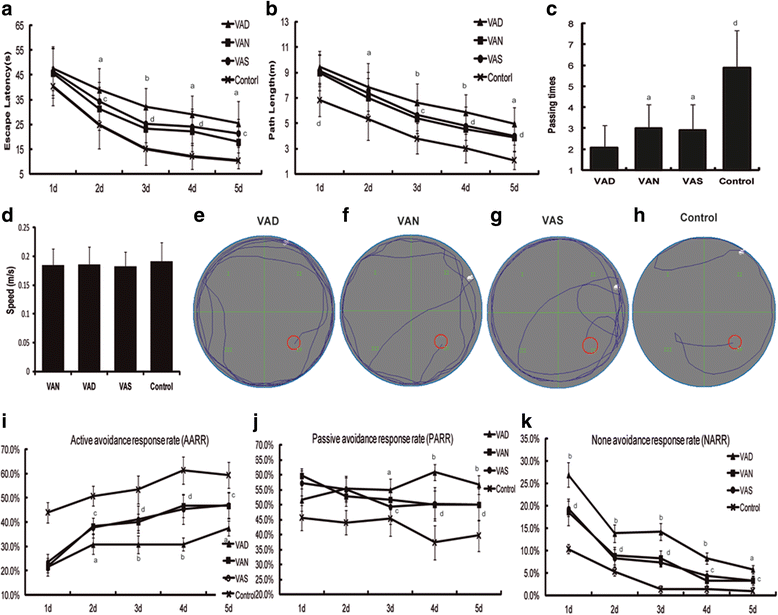
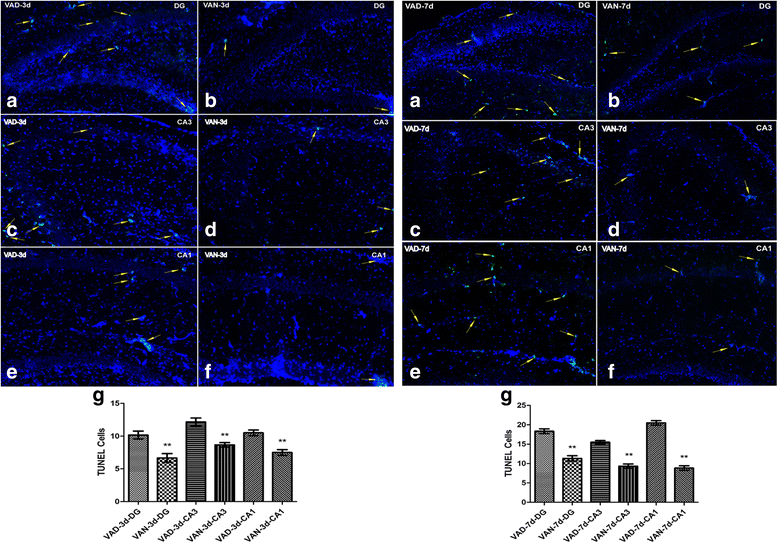
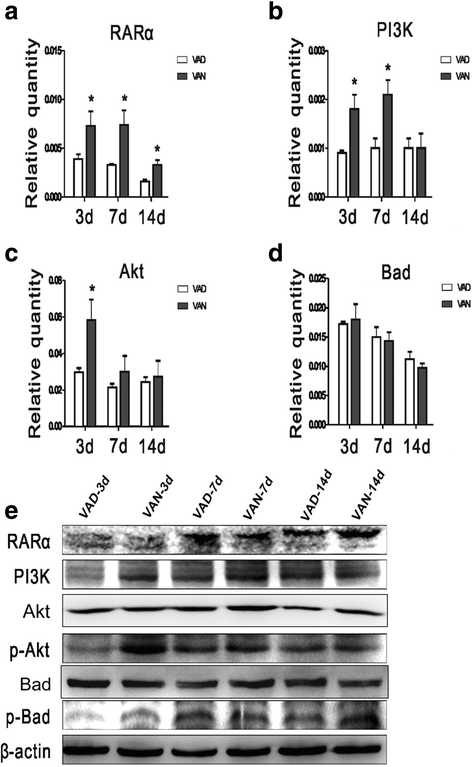
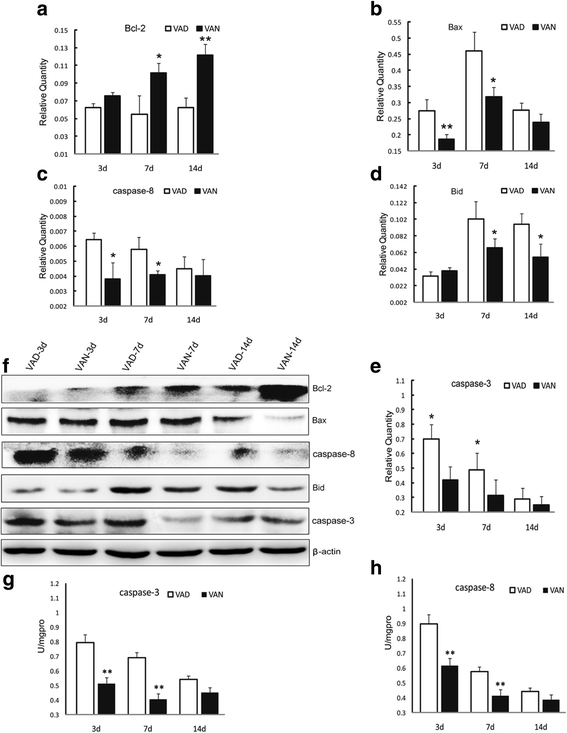
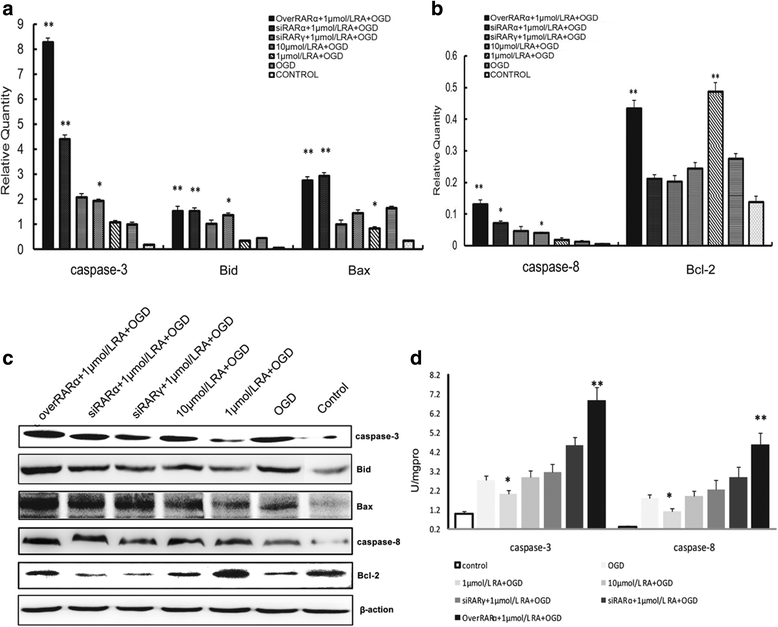
Our previous studies demonstrated that vitamin A deficiency (VAD) can impair the postnatal cognitive function of rats by damaging the hippocampus. The present study examined the effects of retinoic acid (RA) on apoptosis induced by hypoxic-ischemic damage in vivo and in vitro, and investigated the possible signaling pathway involved in the neuroprotective anti-apoptotic effects of RA. Flow cytometry, immunofluorescence staining and behavioral tests were used to evaluate the neuroprotective and anti-apoptotic effects of RA. The protein and mRNA levels of RARα, PI3K, Akt, Bad, caspase-3, caspase-8, Bcl-2, Bax, and Bid were measured with western blotting and real-time PCR, respectively. We found impairments in learning and spatial memory in VAD group compared with vitamin A normal (VAN) and vitamin A supplemented (VAS) group. Additionally, we showed that hippocampal apoptosis was weaker in the VAN group than that in VAD group. Relative to the VAD group, the VAN group also had increased mRNA and protein levels of RARα and PI3K, and upregulated phosphorylated Akt/Bad levels in vivo. In vitro, excessively low or high RA signaling promoted apoptosis. Furthermore, the effects on apoptosis involved the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP). These data support the idea that sustained VAD following hypoxic-ischemic brain damage (HIBD) inhibits RARα, which downregulates the PI3K/Akt/Bad and Bcl-2/Bax pathways and upregulates the caspase-8/Bid pathway to influence the MMP, ultimately producing deficits in learning and spatial memory in adolescence. This suggests that clinical interventions for HIBD should include suitable doses of VA.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Hypoxic-ischemic brain damage (HIBD); Mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP); PI3K/Akt; Retinoic acid (RA); Vitamin A (VA).
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
All animal experiments were approved by the Animal Experimentation Ethical Committee of the Zoology Center at Chongqing Medical University (Chongqing, China) [SCXK (Yu) 2012-0015].
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
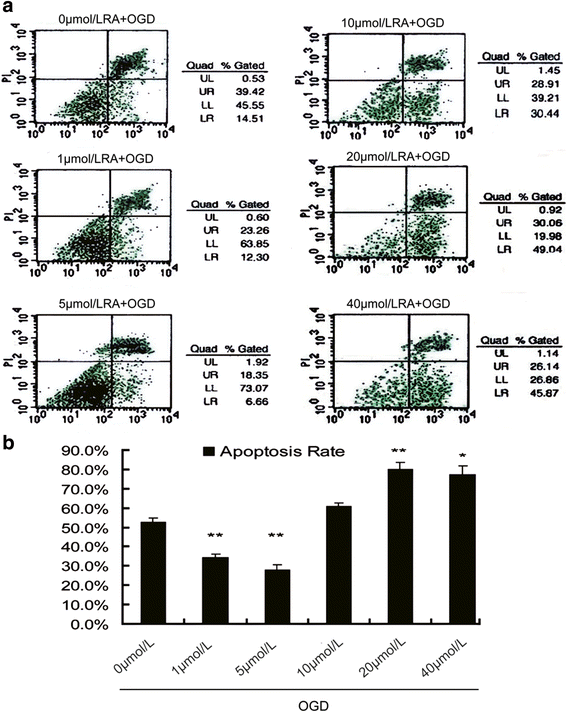
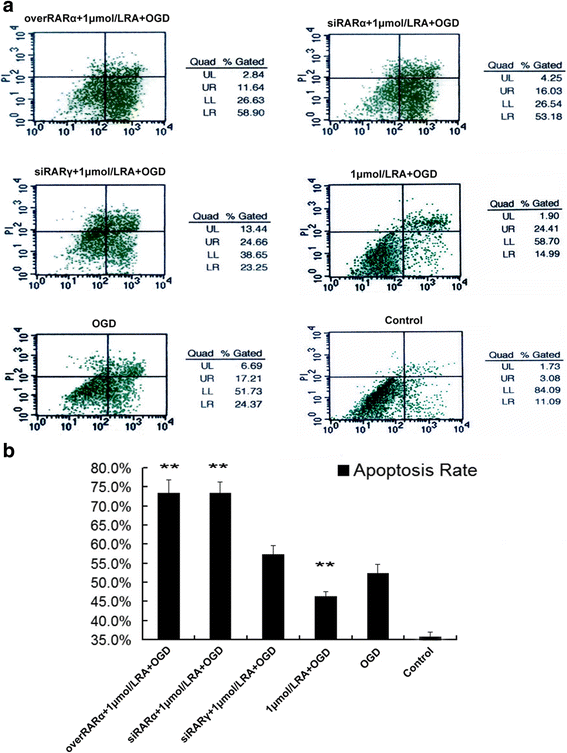
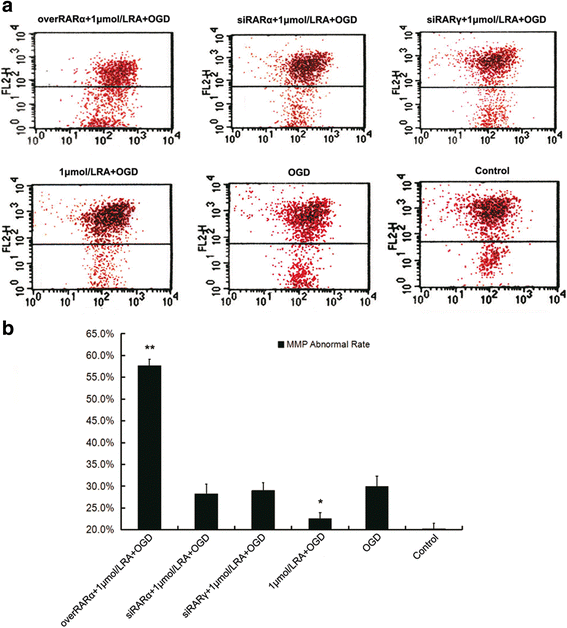
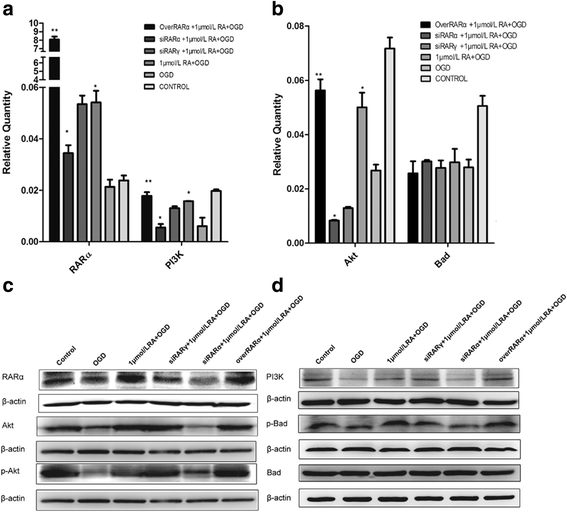
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

