Lipin deactivation after acetaminophen overdose causes phosphatidic acid accumulation in liver and plasma in mice and humans and enhances liver regeneration
- PMID: 29534981
- PMCID: PMC5935563
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fct.2018.03.014
Lipin deactivation after acetaminophen overdose causes phosphatidic acid accumulation in liver and plasma in mice and humans and enhances liver regeneration
Figures
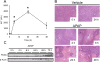
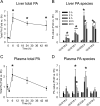
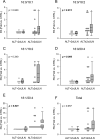
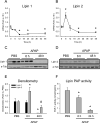

Similar articles
-
Loss of lipin 1-mediated phosphatidic acid phosphohydrolase activity in muscle leads to skeletal myopathy in mice.FASEB J. 2019 Jan;33(1):652-667. doi: 10.1096/fj.201800361R. Epub 2018 Jul 20. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30028636 Free PMC article.
-
Mice with an adipocyte-specific lipin 1 separation-of-function allele reveal unexpected roles for phosphatidic acid in metabolic regulation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jan 8;110(2):642-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1213493110. Epub 2012 Dec 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23267081 Free PMC article.
-
Liver-Specific Deletion of Integrin-Linked Kinase in Mice Attenuates Hepatotoxicity and Improves Liver Regeneration After Acetaminophen Overdose.Gene Expr. 2016;17(1):35-45. doi: 10.3727/105221616X691578. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Gene Expr. 2016. PMID: 27125733 Free PMC article.
-
DAMPs and sterile inflammation in drug hepatotoxicity.Hepatol Int. 2019 Jan;13(1):42-50. doi: 10.1007/s12072-018-9911-9. Epub 2018 Nov 24. Hepatol Int. 2019. PMID: 30474802 Review.
-
[Enzymes involved in the metabolism of diacylglycerol and phosphatidic acid].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 1993 Jun;38(8):1389-95. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 1993. PMID: 8393202 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The development and hepatotoxicity of acetaminophen: reviewing over a century of progress.Drug Metab Rev. 2020 Nov;52(4):472-500. doi: 10.1080/03602532.2020.1832112. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Drug Metab Rev. 2020. PMID: 33103516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diacylglycerol kinase alpha regulates post-hepatectomy liver regeneration.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 2;15(1):555. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84403-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39747625 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers of drug-induced liver injury.Adv Pharmacol. 2019;85:221-239. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2019.02.001. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Adv Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31307588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A phospholipase D2 inhibitor, CAY10594, ameliorates acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury by regulating the phosphorylated-GSK-3β/JNK axis.Sci Rep. 2019 May 10;9(1):7242. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43673-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31076618 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers of drug-induced liver injury: progress and utility in research, medicine, and regulation.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2018 Sep;18(9):797-807. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2018.1508998. Epub 2018 Aug 13. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2018. PMID: 30080986 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Antoine DJ, Jenkins RE, Dear JW, Williams DP, McGill MR, Sharpe MR, Craig DG, Simpson KJ, Jaeschke H, Park BK. Molecular forms of HMGB1 and keratin-18 as mechanistic biomarkers for mode of cell death and prognosis during clinical acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. J Hepatol. 2012;56(5):1070–9. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharyya S, Yan K, Pence L, Simpson PM, Gill P, Letzig LG, Beger RD, Sullivan JE, Kearns GL, Reed MD, Marshall JD, Van Den Anker JN, James LP. Targeted liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of serum acylcarnitines in acetaminophen toxicity in children. Biomark Med. 2014;8(2):147–59. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Budnitz DS, Lovegrove MC, Crosby AE. Emergency department visits for overdoses of acetaminophen-containing products. Am J Prev Med. 2011;40(6):585–92. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

