Regorafenib inhibits tumor progression through suppression of ERK/NF-κB activation in hepatocellular carcinoma bearing mice
- PMID: 29535278
- PMCID: PMC5938429
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20171264
Regorafenib inhibits tumor progression through suppression of ERK/NF-κB activation in hepatocellular carcinoma bearing mice
Abstract
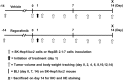
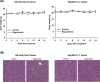
Regorafenib has been demonstrated in our previous study to trigger apoptosis through suppression of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)/nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activation in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) SK-Hep1 cells in vitro However, the effect of regorafenib on NF-κB-modulated tumor progression in HCC in vivo is ambiguous. The aim of the present study is to investigate the effect of regorafenib on NF-κB-modulated tumor progression in HCC bearing mouse model. pGL4.50 luciferase reporter vector transfected SK-Hep1 (SK-Hep1/luc2) and Hep3B 2.1-7 tumor bearing mice were established and used for the present study. Mice were treated with vehicle or regorafenib (20 mg/kg/day by gavage) for 14 days. Effects of regorafenib on tumor growth and protein expression together with toxicity of regorafenib were evaluated with digital caliper and bioluminescence imaging (BLI), ex vivo Western blotting immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining, and measurement of body weight and pathological examination of liver tissue, respectively, in SK-Hep1/luc2 and Hep3B 2.1-7 tumor bearing mice. The results indicated regorafenib significantly reduced tumor growth and expression of phosphorylated ERK, NF-κB p65 (Ser536), phosphorylated AKT, and tumor progression-associated proteins. In addition, we found regorafenib induced both extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways. Body weight and liver morphology were not affected by regorafenib treatment. Our findings present the mechanism of tumor progression inhibition by regorafenib is linked to suppression of ERK/NF-κB signaling in SK-Hep1/luc2 and Hep3B 2.1-7 tumor bearing mice.
Keywords: Bioluminescence imaging; Regorafenib; apoptosis; hepatocellular carcinoma; nuclear factor kappaB.
© 2018 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Regorafenib induces extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis through inhibition of ERK/NF-κB activation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Oncol Rep. 2017 Feb;37(2):1036-1044. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.5328. Epub 2016 Dec 20. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28000898
-
Amentoflavone Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression Through Blockage of ERK/NF-ĸB Activation.In Vivo. 2018 Sep-Oct;32(5):1097-1103. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11351. In Vivo. 2018. PMID: 30150431 Free PMC article.
-
Regorefenib induces extrinsic/intrinsic apoptosis and inhibits MAPK/NF-κB-modulated tumor progression in bladder cancer in vitro and in vivo.Environ Toxicol. 2019 Jun;34(6):679-688. doi: 10.1002/tox.22734. Epub 2019 Feb 25. Environ Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30801954 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted role of NF-κB in hepatocellular carcinoma therapy: Molecular landscape, therapeutic compounds and nanomaterial approaches.Environ Res. 2023 Jul 1;228:115767. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.115767. Epub 2023 Mar 24. Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 36966991 Review.
-
Underlying mechanisms and management strategies for regorafenib-induced toxicity in hepatocellular carcinoma.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2024 Sep;20(9):907-922. doi: 10.1080/17425255.2024.2398628. Epub 2024 Sep 3. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39225462 Review.
Cited by
-
Regorafenib Attenuates Osteoclasts Differentiation by Inhibiting the NF-κB, NFAT, ERK, and p38 Signaling Pathways.ACS Omega. 2024 Jul 23;9(31):33574-33593. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c01308. eCollection 2024 Aug 6. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39130575 Free PMC article.
-
Aurora-B: a novel biomarker in the invasion and metastasis of osteosarcoma.Biomark Med. 2024;18(13-14):639-647. doi: 10.1080/17520363.2024.2366160. Epub 2024 Jul 29. Biomark Med. 2024. PMID: 39069957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical Evaluation of Recombinant Human IL15 Protein Fused with Albumin Binding Domain on Anti-PD-L1 Immunotherapy Efficiency and Anti-Tumor Immunity in Colon Cancer and Melanoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 9;13(8):1789. doi: 10.3390/cancers13081789. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33918641 Free PMC article.
-
Regorafenib prevents the development of emphysema in a murine elastase model.BMB Rep. 2023 Aug;56(8):439-444. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2023-0072. BMB Rep. 2023. PMID: 37357536 Free PMC article.
-
Proteoglycan-4 is correlated with longer survival in HCC patients and enhances sorafenib and regorafenib effectiveness via CD44 in vitro.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Nov 16;11(11):984. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03180-8. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 33199679 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

