Novel 2-pheynlbenzofuran derivatives as selective butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 29535344
- PMCID: PMC5849682
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-22747-2
Novel 2-pheynlbenzofuran derivatives as selective butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
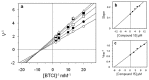
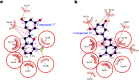
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder representing the leading cause of dementia and is affecting nearly 44 million people worldwide. AD is characterized by a progressive decline in acetylcholine levels in the cholinergic systems, which results in severe memory loss and cognitive impairments. Expression levels and activity of butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) enzyme has been noted to increase significantly in the late stages of AD, thus making it a viable drug target. A series of hydroxylated 2-phenylbenzofurans compounds were designed, synthesized and their inhibitory activities toward acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and BChE enzymes were evaluated. Two compounds (15 and 17) displayed higher inhibitory activity towards BChE with IC50 values of 6.23 μM and 3.57 μM, and a good antioxidant activity with EC50 values 14.9 μM and 16.7 μM, respectively. The same compounds further exhibited selective inhibitory activity against BChE over AChE. Computational studies were used to compare protein-binding pockets and evaluate the interaction fingerprints of the compound. Molecular simulations showed a conserved protein residue interaction network between the compounds, resulting in similar interaction energy values. Thus, combination of biochemical and computational approaches could represent rational guidelines for further structural modification of these hydroxy-benzofuran derivatives as future drugs for treatment of AD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
2-Phenylbenzofuran derivatives as butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors: Synthesis, biological activity and molecular modeling.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016 May 1;26(9):2308-13. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.03.039. Epub 2016 Mar 11. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016. PMID: 26995529
-
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of benzofuran appended benzothiazepine derivatives as inhibitors of butyrylcholinesterase and antimicrobial agents.Bioorg Med Chem. 2018 Jul 23;26(12):3076-3095. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2018.02.049. Epub 2018 Mar 1. Bioorg Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29866481
-
Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of Acetylcholinesterase and Butyrylcholinesterase Dual-Target Inhibitors against Alzheimer's Diseases.Molecules. 2020 Jan 23;25(3):489. doi: 10.3390/molecules25030489. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 31979317 Free PMC article.
-
Cholinesterase Inhibitory Activity of Some semi-Rigid Spiro Heterocycles: POM Analyses and Crystalline Structure of Pharmacophore Site.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018;18(8):711-716. doi: 10.2174/1389557517666170713114039. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 28714400 Review.
-
A molecular approach in drug development for Alzheimer's disease.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Oct;106:553-565. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.147. Epub 2018 Jul 11. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29990843 Review.
Cited by
-
Ugi Reaction Synthesis of Oxindole-Lactam Hybrids as Selective Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibitors.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2021 Jul 23;12(11):1718-1725. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.1c00344. eCollection 2021 Nov 11. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2021. PMID: 34795859 Free PMC article.
-
Action Mechanisms of Curcumin in Alzheimer's Disease and Its Brain Targeted Delivery.Materials (Basel). 2021 Jun 16;14(12):3332. doi: 10.3390/ma14123332. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34208692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective Effect of Terpenoids Recovered from Olive Oil By-Products.Foods. 2021 Jun 29;10(7):1507. doi: 10.3390/foods10071507. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34209864 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial Activity and Molecular Docking Studies of a Selected Series of Hydroxy-3-arylcoumarins.Molecules. 2019 Aug 1;24(15):2815. doi: 10.3390/molecules24152815. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31375003 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Assessment of Cholinesterase Inhibition and Neuroprotective Effects of Elaeocarpus angustifolius Blume Against Amyloid-Beta Peptide-Induced Toxicity in SH-SY5Y and BV-2 Cells.Neurochem Res. 2025 Jul 9;50(4):226. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04478-9. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40632335
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association. Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s & Dementia13, 325–373, 10.1016/j.jalz.2017.02.001 (2017).
-
- Kumar A, Dogra S. Neuropathology and therapeutic management of Alzheimer’s disease - An update. Drugs Future. 2008;33:433. doi: 10.1358/dof.2008.033.05.1192677. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

