Bioimpedance-defined overhydration predicts survival in end stage kidney failure (ESKF): systematic review and subgroup meta-analysis
- PMID: 29535377
- PMCID: PMC5849723
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-21226-y
Bioimpedance-defined overhydration predicts survival in end stage kidney failure (ESKF): systematic review and subgroup meta-analysis
Abstract
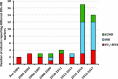
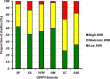
Both overhydration and comorbidity predict mortality in end-stage kidney failure (ESKF) but it is not clear whether these are independent of one another. We undertook a systematic review of studies reporting outcomes in adult dialysis patients in which comorbidity and overhydration, quantified by whole body bioimpedance (BI), were reported. PubMed, EMBASE, PsychInfo and the Cochrane trial database were searched (1990-2017). Independent reviewers appraised studies including methodological quality (assessed using QUIPS). Primary outcome was mortality, with secondary outcomes including hospitalisation and cardiovascular events. Of 4028 citations identified, 46 matched inclusion criteria (42 cohorts; 60790 patients; 8187 deaths; 95% haemodialysis/5% peritoneal dialysis). BI measures included phase angle/BI vector (41%), overhydration index (39%) and extra:intracellular water ratio (20%). 38 of 42 cohorts had multivariable survival analyses (MVSA) adjusting for age (92%), gender (66%), diabetes (63%), albumin (58%), inflammation (CRP/IL6-37%), non-BI nutritional markers (24%) and echocardiographic data (8%). BI-defined overhydration (BI-OH) independently predicted mortality in 32 observational cohorts. Meta-analysis revealed overhydration >15% (HR 2.28, 95% CI 1.56-3.34, P < 0.001) and a 1-degree decrease in phase angle (HR 1.74, 95% CI 1.37-2.21, P < 0.001) predicted mortality. BI-OH predicts mortality in dialysis patients independent of the influence of comorbidity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

