A LATS biosensor screen identifies VEGFR as a regulator of the Hippo pathway in angiogenesis
- PMID: 29535383
- PMCID: PMC5849716
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-03278-w
A LATS biosensor screen identifies VEGFR as a regulator of the Hippo pathway in angiogenesis
Abstract
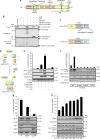
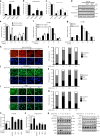
The Hippo pathway is a central regulator of tissue development and homeostasis, and has been reported to have a role during vascular development. Here we develop a bioluminescence-based biosensor that monitors the activity of the Hippo core component LATS kinase. Using this biosensor and a library of small molecule kinase inhibitors, we perform a screen for kinases modulating LATS activity and identify VEGFR as an upstream regulator of the Hippo pathway. We find that VEGFR activation by VEGF triggers PI3K/MAPK signaling, which subsequently inhibits LATS and activates the Hippo effectors YAP and TAZ. We further show that the Hippo pathway is a critical mediator of VEGF-induced angiogenesis and tumor vasculogenic mimicry. Thus, our work offers a biosensor tool for the study of the Hippo pathway and suggests a role for Hippo signaling in regulating blood vessel formation in physiological and pathological settings.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Xu T, Wang W, Zhang S, Stewart RA, Yu W. Identifying tumor suppressors in genetic mosaics: the Drosophila lats gene encodes a putative protein kinase. Development. 1995;121:1053–1063. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

