Bioequivalence of HTX-019 (aprepitant IV) and fosaprepitant in healthy subjects: a Phase I, open-label, randomized, two-way crossover evaluation
- PMID: 29535504
- PMCID: PMC5837372
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S155875
Bioequivalence of HTX-019 (aprepitant IV) and fosaprepitant in healthy subjects: a Phase I, open-label, randomized, two-way crossover evaluation
Abstract
Introduction: Fosaprepitant, an intravenous (IV) aprepitant prodrug for chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting prophylaxis, is associated with systemic and infusion-site reactions attributed in part to its surfactant, polysorbate 80. HTX-019 is an IV aprepitant formulation free of polysorbate 80 and other synthetic surfactants.
Materials and methods: This open-label, single-dose, randomized, two-way crossover bioequivalence study compared pharmacokinetics and safety of HTX-019 and fosaprepitant. Healthy subjects received single-dose HTX-019 (130 mg) or fosaprepitant (150 mg) IV over 30 min, with ≥7-day washout between doses. Blood samples were evaluated for pharmacokinetics and bioequivalence; safety evaluation included treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) and serious adverse events. Ninety-seven of one hundred enrolled subjects completed the study.
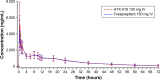
Results: Baseline characteristics were comparable between treatment sequences. For HTX-019, mean (percent coefficient of variation) area under the curve (AUC) from time 0 to time of last measurable plasma concentration (AUC0-t), AUC from time 0 to infinity (AUC0-inf), and plasma concentration at 12 h (C12 h) for HTX-019 were 43,729 h*ng/mL (32.7), 45,460 h*ng/mL (36.8), and 988.4 ng/mL (27.5), respectively; corresponding fosaprepitant values were 44,130 h*ng/mL (32.0), 46,163 h*ng/mL (36.6), and 1,022 ng/mL (28.5). Also, 90% CIs (94.186-101.354) were within bioequivalence bounds (80%-125%). Within 1 h following infusion start, one (1%) HTX-019 recipient reported one TEAE, while 20 (20%) fosaprepitant recipients reported 32 TEAEs. Dyspnea occurred in three fosaprepitant recipients (at <1 min in two subjects and at 18 min in one subject, considered study drug related) and one HTX-019 recipient (at 120 h, associated with a respiratory tract infection and considered not related to the study drug). No severe TEAEs, serious adverse events, or deaths occurred; all TEAEs resolved.
Conclusion: HTX-019 was bioequivalent to fosaprepitant and may provide a safer alternative to fosaprepitant for chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting prophylaxis.
Keywords: antiemetics; polysorbate 80; safety; surfactant.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure TO, MRK, MC, NC, and BQ are Heron Therapeutics, Inc., employees and report stock ownership. TO, NC, and BQ report leadership roles with Heron Therapeutics, Inc. TO reports travel, accommodation, and expenses reimbursed by Heron Therapeutics, Inc. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Bloechl-Daum B, Deuson RR, Mavros P, Hansen M, Herrstedt J. Delayed nausea and vomiting continue to reduce patients’ quality of life after highly and moderately emetogenic chemotherapy despite antiemetic treatment. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(27):4472–4478. - PubMed
-
- Haiderali A, Menditto L, Good M, Teitelbaum A, Wegner J. Impact on daily functioning and indirect/direct costs associated with chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) in a U.S. population. Support Care Cancer. 2011;19(6):843–851. - PubMed
-
- Hesketh PJ, Kris MG, Grunberg SM, et al. Proposal for classifying the acute emetogenicity of cancer chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15(1):103–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

