rs11614913 polymorphism in miRNA-196a2 and cancer risk: an updated meta-analysis
- PMID: 29535537
- PMCID: PMC5840307
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S154211
rs11614913 polymorphism in miRNA-196a2 and cancer risk: an updated meta-analysis
Abstract
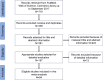
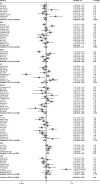
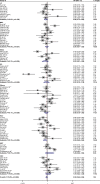
Several epidemiological studies have reported that polymorphisms in microRNA-196a2 (miR-196a2) were associated with various cancers. However, the results remained unverified and were inconsistent in different cancers. Therefore, we carried out an updated meta-analysis to elaborate the effects of rs11614913 polymorphism on cancer susceptibility. A total of 84 articles with 35,802 cases and 41,541 controls were included to evaluate the association between the miR-196a2 rs11614913 and cancer risk by pooled odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). The results showed that miR-196a2 rs11614913 polymorphism is associated with cancer susceptibility, especially in lung cancer (homozygote comparison, OR =0.840, 95% CI =0.734-0.961; recessive model, OR =0.858, 95% CI =0.771-0.955), hepatocellular carcinoma (allelic contrast, OR =0.894, 95% CI =0.800-0.998; homozygote comparison, OR =0.900, 95% CI =0.813-0.997; recessive model, OR =0.800, 95% CI =0.678-0.944), and head and neck cancer (allelic contrast, OR =1.076, 95% CI =1.006-1.152; homozygote comparison, OR =1.214, 95% CI =1.043-1.413). In addition, significant association was found among Asian populations (allele model, OR =0.847, 95% CI =0.899-0.997, P=0.038; homozygote model, OR =0.878, 95% CI =0.788-0.977, P=0.017; recessive model, OR =0.895, 95% CI =0.824-0.972, P=0.008) but not in Caucasians. The updated meta-analysis confirmed the previous results that miR-196a2 rs11614913 polymorphism may serve as a risk factor for patients with cancers.
Keywords: cancer risk; meta-analysis; miR-196a2; polymorphisms.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Liu CJ, Tsai MM, Tu HF, Lui MT, Cheng HW, Lin SC. miR-196a overexpression and miR-196a2 gene polymorphism are prognostic predictors of oral carcinomas. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20(Suppl 3):S406–S414. - PubMed
-
- Tian T, Shu Y, Chen J, et al. A functional genetic variant in microRNA-196a2 is associated with increased susceptibility of lung cancer in Chinese. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prev. 2009;18(4):1183–1187. - PubMed
-
- Peng S, Kuang Z, Sheng C, Zhang Y, Xu H, Cheng Q. Association of microRNA-196a-2 gene polymorphism with gastric cancer risk in a Chinese population. Dig Dis Sci. 2010;55(8):2288–2293. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

