Melatonin-Stimulated Triacylglycerol Breakdown and Energy Turnover under Salinity Stress Contributes to the Maintenance of Plasma Membrane H+-ATPase Activity and K+/Na+ Homeostasis in Sweet Potato
- PMID: 29535758
- PMCID: PMC5835075
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00256
Melatonin-Stimulated Triacylglycerol Breakdown and Energy Turnover under Salinity Stress Contributes to the Maintenance of Plasma Membrane H+-ATPase Activity and K+/Na+ Homeostasis in Sweet Potato
Abstract
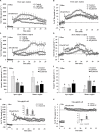
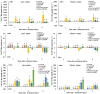
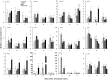
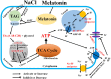
Melatonin (MT) is a multifunctional molecule in animals and plants and is involved in defense against salinity stress in various plant species. In this study, MT pretreatment was simultaneously applied to the roots and leaves of sweet potato seedlings [Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.], which is an important food and industry crop worldwide, followed by treatment of 150 mM NaCl. The roles of MT in mediating K+/Na+ homeostasis and lipid metabolism in salinized sweet potato were investigated. Exogenous MT enhanced the resistance to NaCl and improved K+/Na+ homeostasis in sweet potato seedlings as indicated by the low reduced K+ content in tissues and low accumulation of Na+ content in the shoot. Electrophysiological experiments revealed that exogenous MT significantly suppressed NaCl-induced K+ efflux in sweet potato roots and mesophyll tissues. Further experiments showed that MT enhanced the plasma membrane (PM) H+-ATPase activity and intracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP) level in the roots and leaves of salinized sweet potato. Lipidomic profiling revealed that exogenous MT completely prevented salt-induced triacylglycerol (TAG) accumulation in the leaves. In addition, MT upregulated the expression of genes related to TAG breakdown, fatty acid (FA) β-oxidation, and energy turnover. Chemical inhibition of the β-oxidation pathway led to drastic accumulation of lipid droplets in the vegetative tissues of NaCl-stressed sweet potato and simultaneously disrupted the MT-stimulated energy state, PM H+-ATPase activity, and K+/Na+ homeostasis. Results revealed that exogenous MT stimulated TAG breakdown, FA β-oxidation, and energy turnover under salinity conditions, thereby contributing to the maintenance of PM H+-ATPase activity and K+/Na+ homeostasis in sweet potato.
Keywords: K+/Na+ homeostasis; PM H+–ATPase; fatty acid β-oxidation; melatonin; sweet potato; triacylglycerol.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Involvement of Phosphatidylserine and Triacylglycerol in the Response of Sweet Potato Leaves to Salt Stress.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Sep 10;10:1086. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01086. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31552077 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of phosphatidylserine synthase IbPSS1 affords cellular Na+ homeostasis and salt tolerance by activating plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiport activity in sweet potato roots.Hortic Res. 2020 Aug 1;7:131. doi: 10.1038/s41438-020-00358-1. eCollection 2020. Hortic Res. 2020. PMID: 32821414 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated compartmentalization of Na+ into vacuoles improves salt and cold stress tolerance in sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas).Physiol Plant. 2015 Aug;154(4):560-71. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12301. Epub 2014 Nov 8. Physiol Plant. 2015. PMID: 25307930
-
Exogenous melatonin-mediated regulation of K+ /Na+ transport, H+ -ATPase activity and enzymatic antioxidative defence operate through endogenous hydrogen sulphide signalling in NaCl-stressed tomato seedling roots.Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2021 Sep;23(5):797-805. doi: 10.1111/plb.13296. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2021. PMID: 34263973
-
Root-zone-specific sensitivity of K+-and Ca2+-permeable channels to H2O2 determines ion homeostasis in salinized diploid and hexaploid Ipomoea trifida.J Exp Bot. 2019 Feb 20;70(4):1389-1405. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery461. J Exp Bot. 2019. PMID: 30689932 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Melatonin Positively Influences the Photosynthetic Machinery and Antioxidant System of Avena sativa during Salinity Stress.Plants (Basel). 2019 Dec 16;8(12):610. doi: 10.3390/plants8120610. Plants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31888189 Free PMC article.
-
New insights on neurotransmitters signaling mechanisms in plants.Plant Signal Behav. 2020 Jun 2;15(6):1737450. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2020.1737450. Epub 2020 May 6. Plant Signal Behav. 2020. PMID: 32375557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melatonin: A Small Molecule but Important for Salt Stress Tolerance in Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 7;20(3):709. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030709. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30736409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-throughput deep sequencing reveals the important role that microRNAs play in the salt response in sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.).BMC Genomics. 2020 Feb 17;21(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-6567-3. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32066373 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review of Melatonin in Plants: An Example of Evolution of Literature.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Jun 18;12:683047. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.683047. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34249052 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

