The KDEL receptor signalling cascade targets focal adhesion kinase on focal adhesions and invadopodia
- PMID: 29535802
- PMCID: PMC5828207
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.23421
The KDEL receptor signalling cascade targets focal adhesion kinase on focal adhesions and invadopodia
Abstract
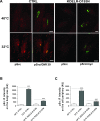
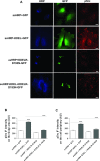
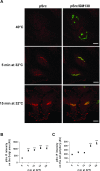
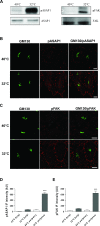
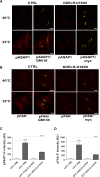
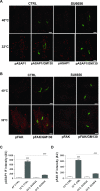
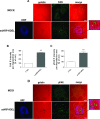
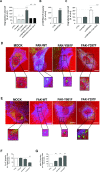
Membrane trafficking via the Golgi-localised KDEL receptor activates signalling cascades that coordinate both trafficking and other cellular functions, including autophagy and extracellular matrix degradation. In this study, we provide evidence that membrane trafficking activates KDEL receptor and the Src family kinases at focal adhesions of HeLa cells, where this phosphorylates ADP-ribosylation factor GTPase-activating protein with SH3 domain, ankyrin repeat and PH domain (ASAP)1 and focal adhesion kinase (FAK). Previous studies have reported extracellular matrix degradation at focal adhesions. Here, matrix degradation was not seen at focal adhesions, although it occurred at invadopodia, where it was increased by KDEL receptor activation. This activation of KDEL receptor at invadopodia of A375 cells promoted recruitment and phosphorylation of FAK on tyrosines 397 and 861. From the functional standpoint, FAK overexpression inhibited steady-state and KDEL-receptor-stimulated extracellular matrix degradation, whereas overexpression of the FAK-Y397F mutant only inhibited KDEL-receptor-stimulated matrix degradation. Finally, we show that the Src and FAK activated downstream of KDEL receptor are part of parallel signalling pathways. In conclusion, membrane-traffic-generated signalling via KDEL receptor activates Src not only at the Golgi complex, but also at focal adhesions. By acting on Src and FAK, KDEL receptor increases invadopodia-mediated matrix degradation.
Keywords: FAK; KDEL receptor; Src; cell signalling; membrane trafficking.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential effect of the focal adhesion kinase Y397F mutant on v-Src-stimulated cell invasion and tumor growth.J Biomed Sci. 2005;12(4):571-85. doi: 10.1007/s11373-005-7212-5. Epub 2005 Nov 10. J Biomed Sci. 2005. PMID: 16132110
-
Focal adhesion kinase is not required for Src-induced formation of invadopodia in KM12C colon cancer cells and can interfere with their assembly.Eur J Cell Biol. 2008 Sep;87(8-9):569-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2008.04.002. Epub 2008 Jun 17. Eur J Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18562041
-
NH2 -terminal fragment of ZF21 protein suppresses tumor invasion via inhibiting the interaction of ZF21 with FAK.Cancer Sci. 2020 Dec;111(12):4393-4404. doi: 10.1111/cas.14665. Epub 2020 Oct 7. Cancer Sci. 2020. PMID: 32976654 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transduction by focal adhesion kinase in cancer.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009 Jun;28(1-2):35-49. doi: 10.1007/s10555-008-9165-4. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009. PMID: 19169797 Review.
-
KDEL Receptors: Pathophysiological Functions, Therapeutic Options, and Biotechnological Opportunities.Biomedicines. 2022 May 25;10(6):1234. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061234. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35740256 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ubiquitin-Specific Protease 22 Plays a Key Role in Increasing Extracellular Vesicle Secretion and Regulating Cell Motility of Lung Adenocarcinoma.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Oct;11(38):e2405731. doi: 10.1002/advs.202405731. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39101247 Free PMC article.
-
Dance of The Golgi: Understanding Golgi Dynamics in Cancer Metastasis.Cells. 2022 Apr 28;11(9):1484. doi: 10.3390/cells11091484. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35563790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salidroside Improves Chronic Stress Induced Depressive Symptoms Through Microglial Activation Suppression.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 8;12:635762. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.635762. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34168556 Free PMC article.
-
KDEL Receptor Trafficking to the Plasma Membrane Is Regulated by ACBD3 and Rab4A-GTP.Cells. 2023 Apr 4;12(7):1079. doi: 10.3390/cells12071079. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37048152 Free PMC article.
-
Signalling pathways and cellular functions of KDEL receptors: implications in cancer biology.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025 Aug 6;82(1):299. doi: 10.1007/s00018-025-05820-8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40767982 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Capitani M, Sallese M. The KDEL receptor: new functions for an old protein. FEBS Lett. 2009;583:3863–3871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2009.10.053 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pulvirenti T, Giannotta M, Capestrano M, Capitani M, Pisanu A, Polishchuk RS, San Pietro E, Beznoussenko GV, Mironov AA, Turacchio G, Hsu VW, Sallese M, Luini A. A traffic-activated Golgi-based signalling circuit coordinates the secretory pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10:912–922. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1751 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ruggiero C, Fragassi G, Grossi M, Picciani B, Di Martino R, Capitani M, Buccione R, Luini A, Sallese M. A Golgi-based KDELR-dependent signalling pathway controls extracellular matrix degradation. Oncotarget. 2015;6:3375–3393. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.3270 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Basbaum CB, Werb Z. Focalized proteolysis: spatial and temporal regulation of extracellular matrix degradation at the cell surface. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996;8:731–738. https://doi.org/S0955-0674(96)80116-5 - PubMed
-
- Chen WT. Proteolytic activity of specialized surface protrusions formed at rosette contact sites of transformed cells. J Exp Zool. 1989;251:167–185. https://doi.org/10.1002/jez.1402510206 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

