Serum levels of miR-320 family members are associated with clinical parameters and diagnosis in prostate cancer patients
- PMID: 29535815
- PMCID: PMC5828216
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.23781
Serum levels of miR-320 family members are associated with clinical parameters and diagnosis in prostate cancer patients
Abstract
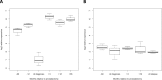
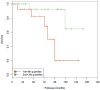
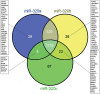
We studied the association of the serum levels of the microRNA family members miR-320a/-b/-c with clinico-pathological data to assess their applicability as diagnostic biomarker in prostate cancer (PCa) patients. The levels of miR-320a/-b/-c in 3 groups were evaluated by qRT-PCR (145 patients with PCa, 31 patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and 19 healthy controls). The levels of the three family members of miR-320 were directly correlated within each group (P < 0.001), but they differed significantly among the three groups (P < 0.001). The serum levels of the miR-320 family members were significantly increased in older patients compared to younger patients (≤ 66 years vs. > 66 years, P ≤ 0.001). In addition, the levels of all three miR-320 family members were significantly different in patients with low tumor stage compared with those with high tumor stage (miR-320a: P = 0.034; miR-320b: P = 0.006; miR-320c: P = 0.007) and in patients with low serum PSA compared with those with high serum PSA (≤ 4 ng vs. > 4 ng; miR-320a: P = 0.003; miR-320b: P = 0.003; miR-320c: P = 0.006). The levels of these miRNAs were inversely correlated with serum PSA levels. Detection in the serum samples of PCa patients with or without PSA relapse revealed higher levels of miR-320a/-b/-c in the group without PSA relapse before/after radical prostatectomy than in that with PCa relapse. In summary, the differences among the PCa/BPH/healthy control groups with respect to miR-320a/-b/-c levels in conjunction with higher levels in patients without a PSA relapse than in those with a relapse suggest the diagnostic potential of these miRNA-320 family members in PCa patients.
Keywords: PSA; diagnosis; miR-320 family; prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST All authors declare to have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The combined serum levels of miR-375 and urokinase plasminogen activator receptor are suggested as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in prostate cancer.Int J Cancer. 2015 Sep 15;137(6):1406-16. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29505. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Int J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25754273
-
MiR-145 detection in urinary extracellular vesicles increase diagnostic efficiency of prostate cancer based on hydrostatic filtration dialysis method.Prostate. 2017 Jul;77(10):1167-1175. doi: 10.1002/pros.23376. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Prostate. 2017. PMID: 28617988
-
Urinary microRNA-based signature improves accuracy of detection of clinically relevant prostate cancer within the prostate-specific antigen grey zone.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Jun;13(6):4549-60. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5095. Epub 2016 Apr 8. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27081843 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-based microRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers to discriminate localized prostate cancer from benign prostatic hyperplasia and allow cancer-risk stratification.Oncol Lett. 2018 Jul;16(1):1357-1365. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8778. Epub 2018 May 22. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30061955 Free PMC article.
-
IGF-II serum levels increase discrimination between benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer and improve the predictive value of PSA in clinical staging.Eur Urol. 2006 Feb;49(2):286-92; discussion 292. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2005.08.022. Epub 2005 Dec 7. Eur Urol. 2006. PMID: 16386354
Cited by
-
miR-320/ELF3 axis inhibits the progression of breast cancer via the PI3K/AKT pathway.Oncol Lett. 2020 Apr;19(4):3239-3248. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11440. Epub 2020 Mar 3. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32256819 Free PMC article.
-
Prostate-derived circulating microRNAs add prognostic value to prostate cancer risk calculators.J Extracell Biol. 2023 Nov;2(11):e122. doi: 10.1002/jex2.122. Epub 2023 Nov 6. J Extracell Biol. 2023. PMID: 38496750 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and Functional Significant of Heat Shock Proteins (HSPs) in Breast Cancer Unveiled by Multi-Omics Approaches.Biology (Basel). 2021 Mar 22;10(3):247. doi: 10.3390/biology10030247. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33810095 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNA-320a-5p contributes to the homeostasis of osteogenesis and adipogenesis in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell.Regen Ther. 2022 Mar 28;20:32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2022.03.001. eCollection 2022 Jun. Regen Ther. 2022. PMID: 35402661 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of plasma exosomal microRNAs with the efficacy of immunotherapy in EGFR/ALK wild-type advanced non-small cell lung cancer.J Immunother Cancer. 2020 Jan;8(1):e000376. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2019-000376. J Immunother Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31959728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tao L, Bei Y, Zhou Y, Xiao J, Li X. Non-coding RNAs in cardiac regeneration. Oncotarget. 2015;6:42613–22. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6073 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Feng B, Chakrabarti S. miR-320 Regulates Glucose-Induced Gene Expression in Diabetes. ISRN Endocrinol. 2012;2012:549875. https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/549875 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yan LX, Huang XF, Shao Q, Huang MY, Deng L, Wu QL, Zeng YX, Shao JY. MicroRNA miR-21 overexpression in human breast cancer is associated with advanced clinical stage, lymph node metastasis and patient poor prognosis. RNA. 2008;14:2348–60. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.1034808 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bronisz A, Godlewski J, Wallace JA, Merchant AS, Nowicki MO, Mathsyaraja H, Srinivasan R, Trimboli AJ, Martin CK, Li F, Yu L, Fernandez SA, Pecot T, et al. Reprogramming of the tumour microenvironment by stromal PTEN-regulated miR-320. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;14:159–67. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2396 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blenkiron C, Hurley DG, Fitzgerald S, Print CG, Lasham A. Links between the oncoprotein YB-1 and small non-coding RNAs in breast cancer. PLoS One. 2013;8:e80171. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0080171 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

