Glycosylation of extracellular vesicles: current knowledge, tools and clinical perspectives
- PMID: 29535851
- PMCID: PMC5844028
- DOI: 10.1080/20013078.2018.1442985
Glycosylation of extracellular vesicles: current knowledge, tools and clinical perspectives
Abstract
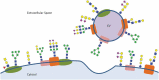
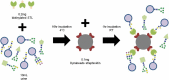
It is now acknowledged that extracellular vesicles (EVs) are important effectors in a vast number of biological processes through intercellular transfer of biomolecules. Increasing research efforts in the EV field have yielded an appreciation for the potential role of glycans in EV function. Indeed, recent reports show that the presence of glycoconjugates is involved in EV biogenesis, in cellular recognition and in the efficient uptake of EVs by recipient cells. It is clear that a full understanding of EV biology will require researchers to focus also on EV glycosylation through glycomics approaches. This review outlines the major glycomics techniques that have been applied to EVs in the context of the recent findings. Beyond understanding the mechanisms by which EVs mediate their physiological functions, glycosylation also provides opportunities by which to engineer EVs for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. Studies characterising the glycan composition of EVs have highlighted glycome changes in various disease states, thus indicating potential for EV glycans as diagnostic markers. Meanwhile, glycans have been targeted as molecular handles for affinity-based isolation in both research and clinical contexts. An overview of current strategies to exploit EV glycosylation and a discussion of the implications of recent findings for the burgeoning EV industry follows the below review of glycomics and its application to EV biology.
Keywords: Extracellular vesicles; exosomes; glycans; glycoengineering; glycomics; glycosylation; lectins; microvesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glycosylation on extracellular vesicles and its detection strategy: Paving the way for clinical use.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Mar;295:139714. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.139714. Epub 2025 Jan 9. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 39798737 Review.
-
Glycosylation of Cancer Extracellular Vesicles: Capture Strategies, Functional Roles and Potential Clinical Applications.Cells. 2021 Jan 8;10(1):109. doi: 10.3390/cells10010109. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33430152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive review of MS-based studies on N-glycoproteome and N-glycome of extracellular vesicles.Proteomics. 2024 Jun;24(11):e2300065. doi: 10.1002/pmic.202300065. Epub 2023 Jul 20. Proteomics. 2024. PMID: 37474487 Review.
-
Glycosylation in extracellular vesicles: Isolation, characterization, composition, analysis and clinical applications.Biotechnol Adv. 2023 Oct;67:108196. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2023.108196. Epub 2023 Jun 10. Biotechnol Adv. 2023. PMID: 37307942 Review.
-
Glycan Profiling Analysis of Equine Amniotic Progenitor Mesenchymal Cells and Their Derived Extracellular Microvesicles.Stem Cells Dev. 2019 Jun 15;28(12):812-821. doi: 10.1089/scd.2019.0013. Epub 2019 Apr 23. Stem Cells Dev. 2019. PMID: 30900531
Cited by
-
Extracellular vesicle depletion and UGCG overexpression mitigate the cell density effect in HEK293 cell culture transfection.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2024 Jan 17;32(1):101190. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2024.101190. eCollection 2024 Mar 14. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2024. PMID: 38327808 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles derived from microgreens of Raphanus sativus L. var. caudatus Alef contain bioactive macromolecules and inhibit HCT116 cells proliferation.Sci Rep. 2022 Sep 20;12(1):15686. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-19950-7. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36127415 Free PMC article.
-
Small Extracellular Vesicles from Human Amniotic Fluid Samples as Promising Theranostics.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 6;23(2):590. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020590. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35054775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered biodistribution of deglycosylated extracellular vesicles through enhanced cellular uptake.J Extracell Vesicles. 2020 Jan 13;9(1):1713527. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2020.1713527. eCollection 2020. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020. PMID: 32082512 Free PMC article.
-
CD147 Promotes Cell Small Extracellular Vesicles Release during Colon Cancer Stem Cells Differentiation and Triggers Cellular Changes in Recipient Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jan 21;12(2):260. doi: 10.3390/cancers12020260. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31973205 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chargaff E, West R.. The biological significance of the thromboplastic protein of blood. J Biol Chem. 1946;166:189–14. - PubMed
-
- Cocucci E, Racchetti G, Meldolesi J.. Shedding microvesicles: artefacts no more. Trends Cell Biol. 2009;19:43–51. - PubMed
-
- Harding C, Stahl P. Transferrin recycling in reticulocytes: pH and iron are important determinants of ligand binding and processing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983;113:650–658. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

