Nordic consensus statement on the systematic assessment and management of possible severe asthma in adults
- PMID: 29535852
- PMCID: PMC5844041
- DOI: 10.1080/20018525.2018.1440868
Nordic consensus statement on the systematic assessment and management of possible severe asthma in adults
Abstract
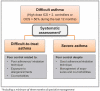
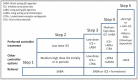
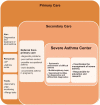
Although a minority of asthma patients suffer from severe asthma, they represent a major clinical challenge in terms of poor symptom control despite high-dose treatment, risk of exacerbations, and side effects. Novel biological treatments may benefit patients with severe asthma, but are expensive, and are only effective in appropriately targeted patients. In some patients, symptoms are driven by other factors than asthma, and all patients with suspected severe asthma ('difficult asthma') should undergo systematic assessment, in order to differentiate between true severe asthma, and 'difficult-to-treat' patients, in whom poor control is related to factors such as poor adherence or co-morbidities. The Nordic Consensus Statement on severe asthma was developed by the Nordic Severe Asthma Network, consisting of members from Norway, Sweden, Finland, Denmark, Iceland and Estonia, including representatives from the respective national respiratory scientific societies with the aim to provide an overview and recommendations regarding the diagnosis, systematic assessment and management of severe asthma. Furthermore, the Consensus Statement proposes recommendations for the organization of severe asthma management in primary, secondary, and tertiary care.
Keywords: Asthma; co-morbidities; diagnosis; guideline; management; prevalence; severe.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Chung KF, Wenzel SE, Brozek JL, et al. International ERS/ATS guidelines on definition, evaluation and treatment of severe asthma. Eur Respir J. 2014;43:343–20. - PubMed
-
- Zeiger RS, Schatz M, Dalal AA, et al. Utilization and costs of severe uncontrolled asthma in a managed-care setting. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2016;4:120–129.e3. - PubMed
-
- Bel EH, Sousa A, Fleming L, et al. Diagnosis and definition of severe refractory asthma: an international consensus statement from the Innovative Medicine Initiative (IMI). Thorax. 2011;66:910–917. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources