The relationship between applied energy and ablation zone volume in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and colorectal liver metastasis
- PMID: 29536242
- PMCID: PMC6028841
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-017-5266-1
The relationship between applied energy and ablation zone volume in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and colorectal liver metastasis
Abstract
Objectives: To study the ratio of ablation zone volume to applied energy in computed tomography (CT)-guided radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and microwave ablation (MWA) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in a cirrhotic liver and in patients with colorectal liver metastasis (CRLM).
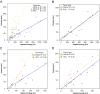
Methods: In total, 90 liver tumors, 45 HCCs in a cirrhotic liver and 45 CRLMs were treated with RFA or with one of two MWA devices (MWA_A and MWA_B), resulting in 15 procedures for each tumor type, per device. Device settings were recorded and the applied energy was calculated. Ablation volumes were segmented on the contrast-enhanced CT scans obtained 1 week after the procedure. The ratio of ablation zone volume in milliliters to applied energy in kilojoules was determined for each procedure and compared between HCC (RHCC) and CRLM (RCRLM), stratified according to ablation device.
Results: With RFA, RHCC and RCRLM were 0.22 mL/kJ (0.14-0.45 mL/kJ) and 0.15 mL/kJ (0.14-0.22 mL/kJ; p = 0.110), respectively. With MWA_A, RHCC was 0.81 (0.61-1.07 mL/kJ) and RCRLM was 0.43 (0.35-0.61 mL/kJ; p = 0.001). With MWA_B, RHCC was 0.67 (0.41-0.85 mL/kJ) and RCRLM was 0.43 (0.35-0.61 mL/kJ; p = 0.040).
Conclusions: With RFA, there was no significant difference in energy deposition ratio between tumor types. With both MWA devices, the ratios were higher for HCCs. Tailoring microwave ablation device protocols to tumor type might prevent incomplete ablations.
Key points: • HCCs and CRLMs respond differently to microwave ablation • For MWA, CRLMs required more energy to achieve a similar ablation volume • Tailoring ablation protocols to tumor type might prevent incomplete ablations.
Keywords: Ablation techniques; Carcinoma, Hepatocellular; Liver diseases; Multidetector computed tomography; Radiology, Interventional.
Conflict of interest statement
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is K.P. de Jong.
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Statistics and biometry
No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was not required for this study because it was a retrospective observational study.
The need for written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was obtained.
Study subjects or cohorts overlap
There is an overlap of 15 patients included in this study and those included in a study by Hof et al. who were treated with RFA for CRLM.
Hof, J., et al. "Outcomes after resection and/or radiofrequency ablation for recurrences after treatment of colorectal liver metastases." British Journal of Surgery 2016;103:1055–1062.
Methodology
• retrospective
• observational
• performed at one institution
Figures

Similar articles
-
CT-monitored minimal ablative margin control in single-session microwave ablation of liver tumors: an effective strategy for local tumor control.Eur Radiol. 2022 Sep;32(9):6327-6335. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-08723-5. Epub 2022 Apr 7. Eur Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35389047 Free PMC article.
-
SAGES/AHPBA guidelines for the use of microwave and radiofrequency liver ablation for the surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma or colorectal liver metastases less than 5 cm.Surg Endosc. 2023 Dec;37(12):8991-9000. doi: 10.1007/s00464-023-10468-1. Epub 2023 Nov 13. Surg Endosc. 2023. PMID: 37957297
-
The pilot experience upon surgical ablation of large liver tumor by microwave system with tissue permittivity feedback control mechanism.BMC Surg. 2014 Oct 22;14:82. doi: 10.1186/1471-2482-14-82. BMC Surg. 2014. PMID: 25336074 Free PMC article.
-
MWA Versus RFA for Perivascular and Peribiliary CRLM: A Retrospective Patient- and Lesion-Based Analysis of Two Historical Cohorts.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2016 Oct;39(10):1438-46. doi: 10.1007/s00270-016-1413-3. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2016. PMID: 27387188 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of microwave ablation and radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Hyperthermia. 2019;36(1):264-272. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2018.1562571. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Int J Hyperthermia. 2019. PMID: 30676100
Cited by
-
Value of spectral detector computed tomography for the early assessment of technique efficacy after microwave ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 15;16(6):e0252678. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252678. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34129650 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic and Robotic Minimally Invasive Thermal Ablation of Malignant Liver Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2021 Sep 23;11:713685. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.713685. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34631539 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Systems and Technologies: State-of-the-Art Applications, Opportunities, and Challenges.IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. 2020;13:325-339. doi: 10.1109/RBME.2019.2908940. Epub 2019 Apr 2. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. 2020. PMID: 30951478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Important parameters should be paid attention in PTMC radiofrequency ablation.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 18;13(1):13450. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-40532-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37596390 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of Two 2.45 GHz Microwave Ablation Devices with Respect to Ablation Zone Volume in Relation to Applied Energy in Patients with Malignant Liver Tumours.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 13;14(22):5570. doi: 10.3390/cancers14225570. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428663 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tanis E, Nordlinger B, Mauer M, et al. Local recurrence rates after radiofrequency ablation or resection of colorectal liver metastases. Analysis of the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer #40004 and #40983. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50:912–919. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2013.12.008. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kao W-Y, Chiou Y-Y, Hung H-H, et al. Risk factors for long-term prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma after radiofrequency ablation therapy: the clinical implication of aspartate aminotransferase-platelet ratio index. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;23:528–536. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

