The Neonatal Behavioral Assessment Scale (NBAS) and Newborn Behavioral Observations (NBO) system for supporting caregivers and improving outcomes in caregivers and their infants
- PMID: 29537066
- PMCID: PMC6494209
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011754.pub2
The Neonatal Behavioral Assessment Scale (NBAS) and Newborn Behavioral Observations (NBO) system for supporting caregivers and improving outcomes in caregivers and their infants
Abstract
Background: The first three years of a child's life are a key period of physical, physiological, cognitive and social development, and the caregiver-infant relationship in early infancy plays an important role in influencing these aspects of development. Specifically, caregiver attunement facilitates the move from coregulation to self-regulation; a parent's ability to understand their infant's behaviour as communication is a key part of this process. Early, brief interventions such as the Neonatal Behavioral Assessment Scale (NBAS) or Neonatal Behavioral Observation (NBO) system are potential methods of improving outcomes for both infant and caregiver.
Objectives: To assess the effects of the NBAS and NBO system for improving caregiver-infant interaction and related outcomes in caregivers and newborn babies. Secondary objectives were to determine whether the NBAS and NBO are more effective for particular groups of infants or parents, and to identify the factors associated with increased effectiveness (e.g. timing, duration, etc.).
Search methods: In September 2017 we searched CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase, PsycINFO, 12 other databases and four trials registers. We also handsearched reference lists of included studies and relevant systematic reviews, and we contacted the Brazelton Institute and searched its websites to identify any ongoing and unpublished studies.
Selection criteria: We included randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and quasi-RCTs that had used at least one standardised measure to assess the effects of the NBAS or NBO versus inactive control for improving outcomes for caregivers and their infants.
Data collection and analysis: Two reviewer authors independently assessed the records retrieved from the search. One reviewer extracted data, and a second checked them for accuracy. We presented the results for each outcome in each study as standardised mean differences (SMDs) or as risk ratios (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). When appropriate, we combined the results in a meta-analysis using standard methodological procedures expected by Cochrane. We used the GRADE approach to assess the overall quality of the body of evidence for each outcome.
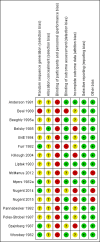
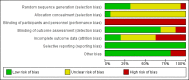
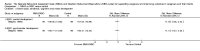
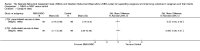
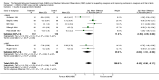
Main results: We identified and included 16 RCTs in this review: 13 assessing the NBAS and 3 the NBO for improving outcomes in 851 randomised participants, including parents and their premature or newborn (aged 4 to 12 weeks) infants. All studies took place in the USA, and we judged all of them to be at high risk of bias.Seven studies involving 304 participants contributed data to one meta-analysis of the impact of the NBAS or NBO for caregiver-infant interaction, and the results suggest a significant, medium-sized difference between intervention and control groups (SMD -0.53, 95% CI -0.90 to -0.17; very low-quality evidence), with moderate heterogeneity (I2 = 51%). Subgroup analysis comparing the two types of programmes (i.e. NBAS and NBO) found a medium but non-significant effect for the NBAS (-0.49, 95% CI -0.99 to 0.00, 5 studies), with high levels of heterogeneity (I2 = 61%), compared with a significant, large effect size for the NBO (-0.69, 95% CI -1.18 to -0.20, 2 studies), with no heterogeneity (I2 = 0.0%). A test for subgroup differences between the two models, however, was not significant. One study found a significant impact on the secondary outcome of caregiver knowledge (SMD -1.30, 95% CI -2.16 to -0.44; very low-quality evidence). There was no evidence of an impact on maternal depression. We did not identify any adverse effects.
Authors' conclusions: There is currently only very low-quality evidence for the effectiveness of the NBAS and NBO in terms of improving parent-infant interaction for mostly low-risk, first-time caregivers and their infants. Further research is underway regarding the effectiveness of the NBO and is necessary to corroborate these results.
Conflict of interest statement
Jane Barlow is an Editor with Cochrane Developmental, Psychosocial and Learning Problems and was Co‐Chair of the Campbell Social Welfare Group until May 2015. Nadeeja INS Herath ‐ none known. Christine Bartram Torrance (CBT) is certified in the Neonatal Behavioral Assessment Scale (NBAS) and Newborn Behavioral Observations (NBO) system. CBT is facilitating the NBAS as part of her collaboration with an observational study in West Africa and will train colleagues in its delivery, for which she will receive payment. In this study, CBT is responsible for conducting NBAS sessions and ensuring handover of her role to local staff members, including ensuring they are trained and certified in the NBAS. Both this review and the observational study are being conducted as part of her PhD. CBT delivers NBAS occasionally on a voluntary basis. CBT is not currently being paid for conducting the NBAS or NBO in her study and has not been paid for conducting them previously in voluntary roles. CBT expects to continue offering these sessions in a voluntary capacity in the future. In terms of support in training others in the NBAS, CBT has not been paid previously, but as CBT is certified, it is possible that she could be paid in the future for training or support in training, or for delivering the sessions in research or support capacities. Cathy Bennett is the proprietor of Systematic Research Ltd. The company received a consultancy fee to enable CB to work as a co‐author of this review. CB has business relationships with other clients, who may provide consultancy fees for evidence‐based medicine reviews, projects and reports. Yinghui Wei ‐ none known.
Figures



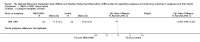
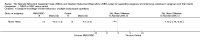
Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Anderson 1981 {published data only}
-
- Anderson CJ. Enhancing reciprocity between mother and neonate. Nursing Research 1981; Vol. 30, issue 2:89‐93. [PUBMED: 6907868] - PubMed
Beal 1989 {published data only}
-
- Beal JA. The effect on father infant interaction of demonstrating the neonatal behavioural assessment scale. Birth 1989; Vol. 16, issue 1:18‐22. [PUBMED: 2742633] - PubMed
Beeghly 1995a {published data only}
-
- Beeghly M, Brazelton TB, Flannery KA, Nugent JK, Barrett DE, Tronick EZ. Specificity of preventative pediatric intervention effects in early infancy. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics 1995; Vol. 16, issue 3:158‐66. [PUBMED: 7560118] - PubMed
Belsky 1985 {published data only}
-
- Belsky J. Experimenting with the family in the newborn period. Child Development 1985; Vol. 56:407‐14. [PUBMED: 3987415] - PubMed
Britt 1994 {published data only}
Furr 1982 {published data only}
Killough 2004 {published data only}
-
- Killough RH. The Birth of Parenting: Maternal Representations, the Place of the Infant, and the Development of Sensitive Caring [PhD thesis]. Amherst: University of Massachusetts Amherst, 2004.
Liptak 1983 {published data only}
-
- Liptak GS, Keller BB, Feldman AW, Chamberlin RW. Enhancing infant development and parent‐practitioner interaction with the Brazelton Neonatal Assessment Scale. Pediatrics 1983; Vol. 72, issue 1:71‐8. [PUBMED: 6866594] - PubMed
McManus 2012 {published data only}
-
- McManus BM, Nugent JK. A neurobehavioral intervention incorporated into a state early intervention program is associated with higher perceived quality of care among parents of high‐risk newborns. Journal of Behavioral Health Services and Research. 2012/04/25 2014; Vol. 41, issue 3:381‐9. [DOI: 10.1007/s11414-012-9283-1; PUBMED: 22529036] - DOI - PubMed
Myers 1982a {published data only}
Nugent 2014 {published data only}
-
- Nugent JK, Bartlett JD, Valim, C. Effects of an infant‐focused relationship‐based hospital and home visiting intervention on reducing symptoms of postpartum maternal depression: a pilot study. Infants and Young Children 2014; Vol. 27, issue 4:292‐304. [DOI: 10.1097/IYC.0000000000000017; 0896‐3746] - DOI
Nugent 2015 {published data only}
-
- Nugent JK, Dym‐Bartlett J, Ende A, Killough J, Valim C. A randomized study of the effects of the Newborn Behavioural Observations (NBO) system on sensitivity in mother‐infant interaction. Society for Research in Child Development Biennial Meeting; 2015 Mar 19‐21; Philadelphia (PA). 2015.
Pannabecker 1982 {published data only}
Poley‐Strobel 1987 {published data only}
-
- Poley‐Strobel BA, Beckmann, CA. The effects of a teaching‐modeling intervention on early mother‐infant reciprocity. Infant Behavior and Development 1987; Vol. 10, issue 4:467‐76. [DOI: 10.1016/0163-6383(87)90043-9] - DOI
Szajnberg 1987 {published data only}
Worobey 1982 {published data only}
-
- Worobey J, Belsky J. Employing the Brazelton scale to influence mothering: an experimental comparison of three strategies. Developmental Psychology 1982; Vol. 18, issue 5:736‐43. [DOI: 10.1037/0012-1649.18.5.736] - DOI
References to studies excluded from this review
Cardone 1990 {published data only}
Cooper 2009 {published data only}
Cooper 2015 {published data only}
-
- Cooper PJ, Pascalis L, Woolgar M, Romaniuk H, Murray L. Attempting to prevent postnatal depression by targeting the mother‐infant relationship: a randomised controlled trial. Primary Health Care Research and Development 2015;16(4):383‐97. [DOI: 10.1017/S1463423614000401; PUBMED: 25381790] - DOI - PubMed
Egeland 1984 {published data only}
-
- Egeland B, Farber EA. Infant‐mother attachment: factors related to its development and changes over time. Child Development 1984;55(3):753‐71. [PUBMED: 6734316] - PubMed
Fowles 1999 {published data only}
-
- Fowles ER. The Brazelton Neonatal Behavioural Assessment Scale and maternal identity. American Journal of Maternal Child Nursing 1999;24(6):287‐93. [PUBMED: 10565142] - PubMed
Golas 1986 {published data only}
Gomes 1987 {published data only}
-
- Gomes‐Pedro J. Early Intervention and Mother‐Infant Interaction During the First Three Months of Life. Washington DC: ERIC Clearinghouse, 1987.
Gomespedro 1995 {published data only}
-
- Gomes‐Pedro J, Patricio M, Carvalho A, Goldschmidt T, Torqal‐Garcia F, Monteiro MB. Early intervention with Portuguese mothers: a two year follow up. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics 1995;16(1):21‐8. [PUBMED: 7730453] - PubMed
Hart 1998 {published data only}
Joshi 2013 {published data only}
-
- Joshi K, Puntambekar A. Effects of early intervention on the behaviour of premature neonates ‐ a clinical trial. Journal of Physical Therapy 2013;8(1):12‐7.
Kiepura 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kiepura E, Kmita G, Cieślak‐Osik B, Urmańska W, Lewandowska D. Neonatal behavioural assessment of pre‐term and full‐term infants as experiences by parents [Ocena zachowania noworodka w doświadczeniu rodziców dzieci urodzonych przedwcześnie i o czasie]. Medycyna Wieku Rozwojowego 2011;15(3 Pt 2):414‐20. [PUBMED: 22253127] - PubMed
Kusaka 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kusaka R, Ohgi S, Gima H, Fujimoto T. Short term effects of the neonatal behavioural assessment scale based intervention for infants with developmental disabilities. Journal of Physical Therapy Science 2007;19(1):1‐8. [DOI: 10.1589/jpts.19.1] - DOI
Meisels 1993 {published data only}
-
- Meisels S, Dichtelmiller M, Liaw FR. A multidimensional analysis of early childhood intervention programme. In: Zeanah CH editor(s). Handbook of Infant Mental Health. 3rd Edition. Vol. 1, Guilford Press, 1993:361‐442.
Nurcombe 1984 {published data only}
Ogi 2001 {published data only}
-
- Ogi S, Arisawa K, Takahashi T, Akiyama T, Goto Y, Fukuda M, et al. The developmental effects of an early intervention programme for very low birthweight infants. Brain and Development 2001;33(1):31‐6. [PUBMED: 11197893] - PubMed
Ohgi 2004 {published data only}
Parker 1992 {published data only}
-
- Parker S, Zahr LK, Cole JG, Brecht ML. Outcome after developmental intervention in the neonatal intensive care unit for mothers of preterm infants with low socioeconomic status. Journal of Paediatrics 1992;120(5):780‐5. [PUBMED: 1578316] - PubMed
Parker Loewen 1987 {published data only}
Sanders 2006 {published data only}
-
- Sanders LW, Buckner EB. The Newborn Behavioral Observations system as a nursing intervention to enhance engagement in first‐time mothers: feasibility and desirability. Pediatric Nursing 2006;32(5):455‐9. [PUBMED: 17100077] - PubMed
Sullivan 1980 {published data only}
-
- Sullivan DL, Leake RD. Significant effect of the Brazelton Neonatal Behavioural Assessment Scale in maternal training. Pediatric Research 1980;14(4):439.
Teti 2009 {published data only}
-
- Teti DM, Black MM, Viscardi R, Glass P, O'Connell MA, Baker L, et al. Intervention with African American premature infants: four months results of an early intervention program. Journal of Early Intervention 2009;31(2):146‐66. [DOI: 10.1177/1053815109331864] - DOI
Wendland Carro 1999 {published data only}
-
- Wendland‐Carro J, Piccinini CA, Millar WS. The role of an early intervention on enhancing the quality of mother‐infant interaction. Child Development 1999;70(3):713‐21. [PUBMED: 10368917] - PubMed
Widmayer 1980 {published data only}
-
- Widmayer SM, Field TM. Effects of Brazelton demonstrations on early interactions of preterm infants and their teenage mothers. Infant Behaviour and Development 1980;3(1):79‐89. [DOI: 10.1016/S0163-6383(80)80008-7] - DOI
Widmayer 1981 {published data only}
-
- Widmayer SM, Field TM. Effects of Brazelton demonstrations for mother on the development of preterm infants. Pediatrics 1981;67(5):711‐4. [PUBMED: 7255001] - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
NCT03070652 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT03070652. What are the effects of supporting early parenting by increasing the understanding of the infant? [What are the effects of supporting early parenting by increasing the understanding of the infant? A randomized community based trial]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03070652 (first received 3 March 2017).
Nicolson 2016 {unpublished data only}
-
- Nicolson S. The UNA Study. Understanding your newborn and adapting to parenthood. Centre for Women's Mental Health. Unpublished manuscript 2016.
Nugent 2016 {unpublished data only}
-
- Nugent JK, McManus B. The effects of the NBO early intervention model of care on infants with developmental disabilities on infant self‐regulation, parent‐infant interaction and maternal depression and later social‐emotional functioning. Unpublished manuscript 2016.
Additional references
Abidin 1983
-
- Abidin RR. The Parenting Stress Index. Charlottesville (VA): Pediatric Psychology Press, 1983.
Ainsworth 1971
-
- Ainsworth MDS, Bell SM, Stayton DJ. Individual differences in strange situation behavior of one‐year‐olds. In: Schaffer HR editor(s). The Origins of Human Social Relations. New York (NY): Academic Press, 1971:17‐57.
Ainsworth 1974
-
- Ainsworth MDS, Bell SM, Stayton DJ. Infant‐mother attachment and social development: socialization as a product of reciprocal responsiveness to signals. In: Richards MPM editor(s). The Integration of a Child into a Social World. London: Cambridge University Press, 1974:97‐119.
Barett 1988
-
- Barett, D, Beeghly, M, Burrows, E, Brazelton TB. Effects of IUGR. Maternal Characteristics and Intervention on Maternal Behaviour with the 4‐month old infant. Infant Association for Infant Mental Health. Providence: RI, 1988.
Barnard 1978
-
- Barnard K. Nursing Child Assessment Teaching Scale. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, 1978.
Bates 1979
Bayley 1969
-
- Bayley N. Bayley Scales of Infant Development: Birth to Two Years. New York: Psychological Corporation, 1969.
Beebe 2010
Beebe 2012
-
- Beebe B, Lachmann F, Jaffe J, Markese S, Buck KA, Chen H, et al. Maternal postpartum depressive symptoms and 4‐month mother‐infant interaction. Psychoanalytic Psychology 2012;29(4):383‐407. [DOI: 10.1037/a0029387] - DOI
Beeghly 1995b
-
- Beeghly M, Brazelton TB, Flannery KA, Nugent JK, Barrett DE, Tronick EZ. Specificity of preventative pediatric intervention effects in early infancy. Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics 1995;16(3):158‐66. [PUBMED: 7560118] - PubMed
Belsky 1984
Belsky 1996
-
- Belsky J, Campbell SB, Cohn JF, Moore G. Instability of infant‐parent attachment security. Developmental Psychology 1996;32(5):921‐4. [DOI: 10.1037//0012-1649.32.5.921] - DOI
Belsky 2002
-
- Belsky J, Fearon RM. Infant‐mother attachment security, contextual risk, and early development: a moderational analysis. Development and Psychopathology 2002;14(2):293‐310. [PUBMED: 12030693] - PubMed
Berlin 2008
-
- Berlin LJ, Cassidy J, Appleyard KC, Shaver PR. The influence of early attachments on other relationships. Handbook of Attachment: Theory, Research, and Clinical Applications. 2nd Edition. New York (US): Guilford Press, 2008:333‐47.
Borelli 2010
-
- Borelli JL, David DH, Crowley MJ, Mayes LC. Links between disorganized attachment classification and clinical symptoms in school‐aged children. Journal of Child and Family Studies 2010;19(3):243‐56. [DOI: 10.1007/s10826-009-9292-8] - DOI
Bornstein 2013
Bowlby 1969
-
- Bowlby J. Attachment and Loss: Vol. 1. Attachment. New York: Basic Books, 1969.
Brazelton 1978
-
- Brazelton TB. The Brazelton Neonatal Behavior Assessment Scale: introduction. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development 1978;43(5‐6):1‐13. [PUBMED: 752799] - PubMed
Brazelton 1995
-
- Brazelton TB. Neonatal Behavioral Assessment Scale. 3rd Edition. London: Mac Keith Press, 1995.
Britt 1994a
Britt 1994b
Broussard 1970
Broussard 1971
-
- Broussard E, Hartner M. Considerations regarding maternal perception of first born. In: Helmuth J editor(s). Exceptional Infants. Vol. 3, New York: Brunner/Mazel, 1971.
Carey 1978
-
- Carey WB, McDevitt SC. Revision of the Infant Temperament Questionnaire. Pediatrics 1978;61:735‐9. [PUBMED: 662513] - PubMed
Clarke‐Stewart 1973
Cooper 2002
-
- Cooper PJ, Landman M, Tomlinson M, Molteno C, Swartz L, Murray L. Impact of a mother‐infant intervention in an indigent peri‐urban South African context: pilot study. British Journal of Psychiatry 2002;180:76‐81. [PUBMED: 11772856] - PubMed
Cox 1987
Crittenden 2001
-
- Crittenden PM. CARE‐Index: Coding Manual. Miami: Family Relations Institute, 2001.
Crockenberg 1982
-
- Crockenberg SB, Smith P. Antecedents of mother‐infant interaction and infant irritability in the first three months of life. Infant Behavior and Development 1982;5(2‐4):105‐19. [DOI: 10.1016/S0163-6383(82)80021-0] - DOI
Das Eiden 1996
-
- Das Eiden R, Reifman A. Effects of Brazelton demonstrations on later parenting: a meta‐analysis. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 1996;21(6):857‐68. [PUBMED: 8990729] - PubMed
De Wolff 1997
-
- Wolff MS, Ijzendoorn MH. Sensitivity and attachment: a meta‐analysis on parental antecedents of infant attachment. Child Development 1997;68(4):571‐91. [PUBMED: 9306636] - PubMed
DeGangi 2000
-
- DeGangi GA, Breinbauer C, Doussard Roosevelt JD, Porges S, Greenspan S. Prediction of childhood problems at three years in children experiencing disorders of regulation during infancy. Journal of Infant Mental Health 2000;21(3):156‐75. [DOI: 10.1002/1097-0355(200007)21:3%3C156::AID-IMHJ2%3E3.0.CO;2-D] - DOI
Dutra 2005
-
- Dutra L, Lyons‐Ruth K. Maltreatment, maternal and child psychopathology, and quality of early care as predictors of adolescent dissociation. Society for Research in Child Development Biennial Meeting; 2005 Apr 7‐10; Atlanta (GA). 2005.
Eshel 2006
Fearon 2010
-
- Fearon RP, Bakermans‐Kranenburg MJ, Ijzendoor MH, Lapsley AM, Roisman GI. The significance of insecure attachment and disorganization in the development of children's externalizing behavior: a meta‐analytic study. Child Development 2010;81(2):435‐56. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.2009.01405.x; PUBMED: 20438450] - DOI - PubMed
Field 1978
-
- Field T, Rydberg Dempsey J, Hayward Hallock N, Shuman HH. The mother's assessment of the behavior of her infants. Infant Behaviour and Development 1978;1:156‐67. [DOI: 10.1016/S0163-6383(78)80026-5] - DOI
Frankenburg 1967
Gaertner 2007
GRADEpro GDT 2015 [Computer program]
-
- McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime). GRADEpro GDT. Version accessed 10 August 2015. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), 2015.
Granot 2001
-
- Granot D, Mayseless O. Attachment security and adjustment to school in middle childhood. International Journal of Behavioral Development 2001;25(6):530‐41. [DOI: 10.1080/01650250042000366] - DOI
Green 2002
-
- Green J, Goldwyn R. Annotation: attachment disorganisation and psychopathology: new findings in attachment research and their potential implications for developmental psychopathology in childhood. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 2002;43(7):835‐46. [PUBMED: 12405473] - PubMed
Greinenberger 2005
-
- Grienenberger JF, Kelly K, Slade A. Maternal reflective functioning, mother‐infant affective communication, and infant attachment: exploring the link between mental states and observed caregiving behavior in the intergenerational transmission of attachment. Attachment and Human Development 2005;7(3):299‐311. [DOI: 10.1080/14616730500245963; PUBMED: 16210241] - DOI - PubMed
Grossman 2002
-
- Grossmann K, Grossmann K, Winter M, Zimmermann P. Attachment relationships and appraisal of partnership: from early experience of sensitive support to later relationship representation. In: Pulkkinen L, Caspi A editor(s). Paths to Successful Development. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2002:73‐105.
Gunnar 1996
Gunnar 2002
-
- Gunnar MR, Donzella B. Social regulation of the cortisol levels in early human development. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2002;27(1‐2):199‐220. [PUBMED: 11750779] - PubMed
Gunnar 2007
Hawthorne 2004
-
- Hawthorne J. Training health professionals in the Neonatal Behavioral Assessment Scale (NBAS) and its use as an intervention. The Signal: Newsletter of the World Association for Infant Mental Health 2004; Vol. 12, issue 3 & 4:1‐36.
Hawthorne 2005
-
- Hawthorne J. Using the Neonatal Behavioral Assessment Scale to support parent‐infant relationships. Infant 2005;1(6):213‐8.
Higgins 2002
Higgins 2016
-
- Higgins JPT, Lasserson T, Chandler J, Tovey D, Churchill R. Methodological Expectations of Cochrane Intervention Reviews (MECIR) Version 1.05. Cochrane, 2016. Available from community.cochrane.org/mecir‐manual.
Higgins 2017
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC, editor(s). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Churchill R, Chandler J, Cumpston MS, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.2.0 (updated June 2017). Cochrane, 2017. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Isabella 1994
-
- Isabella RA. Origins of maternal role satisfaction and its influences upon maternal interactive behavior and infant‐mother attachment. Infant Behavior and Development 1994;17(4):381‐7. [DOI: 10.1016/0163-6383(94)90030-2] - DOI
Jacobvitz 1997
-
- Jacobvitz D, Hazen NL, Riggs S. Disorganized mental processes in mothers, frightened/frightening behavior in caregivers, and disoriented, disorganized behavior in infancy. Society for Research in Child Development Biennial Meeting; 1997; Washington (DC) 1997;17:329‐47.
Keren 2001
Klaus 1972
Koniak‐Griffin 1999
-
- Koniak‐Griffin D, Mathenge C, Anderson NL, Verzemnieks I. An early intervention program for adolescent mothers: a nursing demonstration project. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic and Neonatal Nursing 1999;28(1):51‐9. [PUBMED: 9924864] - PubMed
Koniak‐Griffin 2000
-
- Koniak‐Griffin D, Anderson NL, Verzemnieks I, Brecht ML. A public health nursing early intervention program for adolescent mothers: outcomes from pregnancy through 6 weeks postpartum. Nursing Research 2000;49(3):130‐8. [PUBMED: 10882317] - PubMed
Koniak‐Griffin 2002
-
- Koniak‐Griffin D, Anderson NL, Brecht ML, Verzemnieks I, Lesser J, Kim S. Public health nursing care for adolescent mothers: impact on infant health and selected maternal outcomes at 1 year postbirth. Journal of Adolescent Health 2002;30(1):44‐54. [PUBMED: 11755800] - PubMed
Koniak‐Griffin 2003
-
- Koniak‐Griffin D, Verzemnieks IL, Anderson NL, Brecht ML, Lesser J, Kim S, et al. Nurse visitation for adolescent mothers: two‐year infant health and maternal outcomes. Nursing Research 2003;52(2):127‐36. [PUBMED: 12657988] - PubMed
Lecce 2008
-
- Lecce S. Attachment and Subjective Well‐Being: the Mediating Role of Emotional Processing and Regulation [PhD thesis]. Toronto: University of Toronto, 2008.
Liptak 1977
-
- Liptak, GS, Hulka BS, Cassel JC. Effectiveness of physician‐mother interactions during infancy. Pediatrics 1977;60:186‐192. [PUBMED: 887332] - PubMed
Lyons‐Ruth 2005
-
- Lyons‐Ruth K, Yellin C, Melnick S, Atwood G. Expanding the concept of unresolved mental states: hostile/helpless states of mind on the Adult Attachment Interview are associated with disrupted mother‐infant communication and infant disorganization. Development and Psychopathology 2005;17(1):1‐23. [PMC1857275; PUBMED: 15971757] - PMC - PubMed
MacDonald 2008
-
- MacDonald HZ, Beeghly M, Grant‐Knight W, Augustyn M, Woods RW, Cabral H, et al. Longitudinal association between infant disorganized attachment and childhood posttraumatic stress symptoms. Development and Psychopathology 2008;20(2):493‐508. [DOI: 10.1017/S0954579408000242; PMC2430632; PUBMED: 18423091] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Malekpour 2007
-
- Malekpour M. Effects of attachment on early and later development. British Journal of Developmental Disabilities 2007;53 Part 2(105):81‐95. [DOI: 10.1179/096979507799103360] - DOI
Markova 2006
McCarthy 1972
-
- McCarthy D. McCarthy Scales of Children's Abilities. New York: Psychological Corporation, 1972.
Meins 2001
-
- Meins E, Fernyhough C, Fradley E, Tuckey M. Rethinking maternal sensitivity: mothers' comments on infants' mental processes predict security of attachment at 12 months. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 2001;42(5):637‐48. [PUBMED: 11464968] - PubMed
Meins 2012
-
- Meins E, Fernyhough C, Rosnay M, Arnott B, Leekam SR, Turner M. Mind‐mindedness as a multidimensional construct: appropriate and non‐attuned mind‐related comments independently predict infant‐mother attachment in a socially diverse sample. Infancy 2012;17(4):393‐415. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1532-7078.2011.00087.x] - DOI - PubMed
Moher 2009
Myers 1982b
-
- Myers BJ. Early intervention using Brazelton training with middle‐class mothers and fathers of newborns. Child Development 1982;53(2):462‐71. [PUBMED: 7075329] - PubMed
NHS England 2014
-
- NHS England. National Health Visiting Service Specification 2014/15. www.england.nhs.uk/wp‐content/uploads/2014/03/hv‐serv‐spec.pdf (accessed March 2014).
Nugent 2003
-
- Nugent, JK. Home Visiting Index. Boston: Brazelton Institute Children's Hospital, 2003.
Nugent 2007
-
- Nugent JK, Keefer CH, Minear S, Johnson LC, Blanchard Y. Understanding Newborn behaviour and Early Relationships: The Newborn Behavioral Observations (NBO) System Handbook. London: Paul H Brookes Publishing, 2007.
Nugent 2017 [pers comm]
-
- Nugent K. Request for information on potential unpublished studies [personal communication]. Email to: J Barlow 13 June 2017.
Porges 2011
-
- Porges SW. The Polyvagal Theory: Neurophysiological Foundations of Emotions, Attachment, Communication and Self‐regulation. New York (NY): WW Norton & Company, Inc, 2011.
Price 1977
-
- Price GM. The Price Adaptation Scale. Unpublished manuscript 1977.
Price 1983
-
- Price, GM. Sensitivity in mother‐infant interactions: the AMIS scale. Infant Behaviour and Development 1983;6(2‐3):353‐60. [DOI: 10.1016/S0163-6383(83)80043-5] - DOI
Rauh 1988
-
- Rauh VA, Achenbach TM, Nurcombe B, Howell CT, Teti DM. Minimizing adverse effects of low birthweight: four‐year results of an early intervention. Child Development 1988;59(3):544‐53. [PUBMED: 2454783] - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Richard 1972
-
- Richard MPM, Bernal JF. An observational study of mother‐infant interaction. In: Blurton‐Jones N editor(s). Ethological studies of Child Behaviour. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1972.
Richter 2004
-
- Richter L. The Importance of Caregiver‐Child Interactions for the Survival and Healthy Development of Young Children: A Review. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2004.
Schore 2001
Schore 2002
-
- Schore AN. Advances in neuropsychoanalysis, attachment theory, and trauma research: implications for self psychology. Psychoanalytic Inquiry 2002;22(3):433‐84. [DOI: 10.1080/07351692209348996] - DOI
Schore 2008
-
- Schore JR, Schore AN. Modern attachment theory: the central role of affect regulation in development and treatment. Clinical Social Work Journal 2008;36(1):9‐20. [DOI: 10.1007/s10615-007-0111-7] - DOI
Seashore 1973
-
- Seashore MJ, Leifer AD, Barnett CR, Leiderman PH. The effects of denial of early mother‐infant interaction on maternal self‐confidence. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 1973;26:369‐78. - PubMed
Shea 1988
-
- Shea E, Tronick Z. The maternal self‐report inventory: a research and clinical instrument for assessing maternal self‐esteem. In: Fitzgerald HE, Lester BE, Yogman MW editor(s). Theory and Research in Behavioral Pediatrics. New York: Plenum Press, 1988:101‐40.
Slade 2001
-
- Slade A, Grienenberger J, Bernbach E, Levy D, Locker A. Maternal reflective functioning and attachment: considering the transmission gap. Paper presented at the Biennial Meeting of the Society for Research on Child Development; 2001 April; Minneapolis (MN). 2001.
Slade 2004
-
- Slade AAJ, Berger B, Bresgi I, Kaplan M. The Parent Development Interview ‐ Revised. New York: The City University of New York, 2004.
Slade 2005
Sroufe 2005
-
- Sroufe A, Egeland B, Carlson E, Collins W. Placing early attachment experiences in developmental context: the Minnesota Longitudinal Study. In: Grossman K, Grossmann K, Waters E editor(s). Attachment from Infancy to Adulthood. New York: The Guilford Press, 2005:48‐70.
Steele 2010
Stern 1998
-
- Stern DN, Bruschweiler‐Stern N, Freeland A. The Birth of a Mother: How the Motherhood Experience Changes You Forever. New York (NY): Basic Books, 1998.
Sumner 1994
-
- Sumner G, Spietz A. NCAST Caregiver/Parent‐Child Interaction Feeding Manual. Seattle: University of Washington, 1994.
Teti 1996
Vondra 2001
-
- Vondra JI, Shaw DS, Swearingen L, Cohen M, Owens EB. Attachment stability and emotional and behavioral regulation from infancy to preschool age. Development and Psychopathology 2001;13(1):13‐33. [PUBMED: 11346048] - PubMed
Waters 2000
-
- Waters E, Merrick S, Treboux D, Crowell J, Albersheim L. Attachment security in infancy and early adulthood: a twenty‐year longitudinal study. Child Development 2000;71(3):684‐9. [PUBMED: 10953934] - PubMed
WAVE Trust 2013
-
- WAVE Trust, Department of Education. Conception to age 2 ‐ the age of opportunity: framework for local area service commissioners. www.wavetrust.org/sites/default/files/reports/conception‐to‐age‐2‐framew... (accessed March 2013).
Weinfield 2000
-
- Weinfield NS, Sroufe LA, Egeland B. Attachment from infancy to early adulthood in a high‐risk sample: continuity, discontinuity, and their correlates. Child Development 2000;71(3):695‐702. [PUBMED: 10953936] - PubMed
Worobey 1985
-
- Worobey J. A review of Brazelton‐based interventions to enhance parent‐infant interaction. Journal of Reproductive and Infant Psychology 1985;3(2):64‐73. [DOI: 10.1080/02646838508403464] - DOI
References to other published versions of this review
Bartram 2016
-
- Bartram SC, Barlow J, Wolke D. The Neonatal Behavioral Assessment Scale (NBAS) and Newborn Behavioral Observations system (NBO) for supporting caregivers and improving outcomes in caregivers and their infants. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 6. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011754] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

