Radiation dose optimisation for conventional imaging in infants and newborns using automatic dose management software: an application of the new 2013/59 EURATOM directive
- PMID: 29537302
- PMCID: PMC6223298
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20180022
Radiation dose optimisation for conventional imaging in infants and newborns using automatic dose management software: an application of the new 2013/59 EURATOM directive
Abstract
Objective: The new 2013/59 EURATOM Directive (ED) demands dosimetric optimisation procedures without undue delay. The aim of this study was to optimise paediatric conventional radiology examinations applying the ED without compromising the clinical diagnosis.
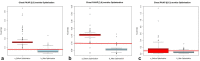
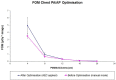
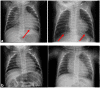
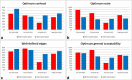
Methods: Automatic dose management software (ADMS) was used to analyse 2678 studies of children from birth to 5 years of age, obtaining local diagnostic reference levels (DRLs) in terms of entrance surface air kerma. Given local DRL for infants and chest examinations exceeded the European Commission (EC) DRL, an optimisation was performed decreasing the kVp and applying the automatic control exposure. To assess the image quality, an analysis of high-contrast resolution (HCSR), signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and figure of merit (FOM) was performed, as well as a blind test based on the generalised estimating equations method.
Results: For newborns and chest examinations, the local DRL exceeded the EC DRL by 113%. After the optimisation, a reduction of 54% was obtained. No significant differences were found in the image quality blind test. A decrease in SNR (-37%) and HCSR (-68%), and an increase in FOM (42%), was observed.
Conclusion: ADMS allows the fast calculation of local DRLs and the performance of optimisation procedures in babies without delay. However, physical and clinical analyses of image quality remain to be needed to ensure the diagnostic integrity after the optimisation process. Advances in knowledge: ADMS are useful to detect radiation protection problems and to perform optimisation procedures in paediatric conventional imaging without undue delay, as ED requires.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Radiation dose management systems-requirements and recommendations for users from the ESR EuroSafe Imaging initiative.Eur Radiol. 2021 Apr;31(4):2106-2114. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07290-x. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 32959080 Free PMC article.
-
OPTIMISATION OF PATIENT DOSE AND IMAGE QUALITY IN FLUOROSCOPICALLY GUIDED CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: A PHANTOM-BASED STUDY.Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2019 Aug 1;184(2):237-247. doi: 10.1093/rpd/ncy205. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2019. PMID: 30508126
-
Optimisation of radiation dose and image quality in mobile neonatal chest radiography.Radiography (Lond). 2018 May;24(2):104-109. doi: 10.1016/j.radi.2017.09.004. Epub 2017 Oct 3. Radiography (Lond). 2018. PMID: 29605105
-
A framework for optimising the radiographic technique in digital X-ray imaging.Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2005;114(1-3):220-9. doi: 10.1093/rpd/nch562. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2005. PMID: 15933112
-
Using diagnostic reference levels to evaluate the improvement of patient dose optimisation and the influence of recent technologies in radiography and computed tomography.Eur J Radiol. 2018 Jan;98:68-74. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2017.11.002. Epub 2017 Nov 7. Eur J Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29279172
References
-
- ICRP. Radiological protection in paediatric diagnostic and interventional radiology. ICRP Publication 121. Ann. ICRP 42; 2013. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

