A zebrafish model of infection-associated acute kidney injury
- PMID: 29537312
- PMCID: PMC6139521
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00328.2017
A zebrafish model of infection-associated acute kidney injury
Abstract
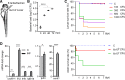
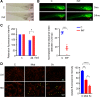
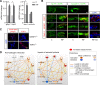
Sepsis-associated acute kidney injury (S-AKI) independently predicts mortality among critically ill patients. The role of innate immunity in this process is unclear, and there is an unmet need for S-AKI models to delineate the pathophysiological response. Mammals and zebrafish ( Danio rerio) share a conserved nephron structure and homologous innate immune systems, making the latter suitable for S-AKI research. We introduced Edwardsiella tarda to the zebrafish. Systemic E. tarda bacteremia resulted in sustained bacterial infection and dose-dependent mortality. A systemic immune reaction was characterized by increased mRNA expressions of il1b, tnfa, tgfb1a, and cxcl8-l1 ( P < 0.0001, P < 0.001, P < 0.001, and P < 0.01, respectively). Increase of host stress response genes ccnd1 and tp53 was observed at 24 h postinjection ( P < 0.0001 and P < 0.05, respectively). Moderate E. tarda infection induced zebrafish mortality of over 50% in larvae and 20% in adults, accompanied by pericardial edema in larvae and renal dysfunction in both larval and adult zebrafish. Expression of AKI markers insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-7 (IGFBP7), tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 2 (TIMP-2), and kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) was found to be significantly increased in the septic animals at the transcription level ( P < 0.01, P < 0.05, and P < 0.05) and in nephric tubules compared with noninfected animals. In conclusion, we established a zebrafish model of S-AKI induced by E. tarda injection, with both larval and adult zebrafish showing nephron injury in the setting of infection.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; innate immunity; zebrafish infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of static immersion and intravenous injection systems for exposure of zebrafish embryos to the natural pathogen Edwardsiella tarda.BMC Immunol. 2011 Oct 17;12:58. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-12-58. BMC Immunol. 2011. PMID: 22003892 Free PMC article.
-
Edwardsiella tarda-Induced Inhibition of Apoptosis: A Strategy for Intracellular Survival.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016 Jul 14;6:76. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00076. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27471679 Free PMC article.
-
Role of intestinal inflammation in predisposition of Edwardsiella tarda infection in zebrafish (Danio rerio).Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014 Dec;41(2):271-8. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2014.09.009. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25224880
-
The role of innate immunity in septic acute kidney injuries.Shock. 2010 Sep;34 Suppl 1:22-6. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e3181e7e69e. Shock. 2010. PMID: 20523275 Review.
-
Edwardsiella tarda - virulence mechanisms of an emerging gastroenteritis pathogen.Microbes Infect. 2012 Jan;14(1):26-34. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2011.08.005. Epub 2011 Sep 1. Microbes Infect. 2012. PMID: 21924375 Review.
Cited by
-
Kidney Injury Molecule 1 (KIM-1): a Multifunctional Glycoprotein and Biological Marker (Review).Sovrem Tekhnologii Med. 2021;13(3):64-78. doi: 10.17691/stm2021.13.3.08. Epub 2021 Jun 28. Sovrem Tekhnologii Med. 2021. PMID: 34603757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zebrafish-based platform for emerging bio-contaminants and virus inactivation research.Sci Total Environ. 2023 May 10;872:162197. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162197. Epub 2023 Feb 11. Sci Total Environ. 2023. PMID: 36781138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Experimental models of acute kidney injury for translational research.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2022 May;18(5):277-293. doi: 10.1038/s41581-022-00539-2. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35173348 Review.
-
The benefits, limitations and opportunities of preclinical models for neonatal drug development.Dis Model Mech. 2022 Apr 1;15(4):dmm049065. doi: 10.1242/dmm.049065. Epub 2022 Apr 25. Dis Model Mech. 2022. PMID: 35466995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Minimal change disease and subacute interstitial nephritis in association with Edwardsiella tarda gastroenteritis following oyster consumption.IDCases. 2021 Jul 24;25:e01236. doi: 10.1016/j.idcr.2021.e01236. eCollection 2021. IDCases. 2021. PMID: 34377670 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chiba T, Skrypnyk NI, Skvarca LB, Penchev R, Zhang KX, Rochon ER, Fall JL, Paueksakon P, Yang H, Alford CE, Roman BL, Zhang MZ, Harris R, Hukriede NA, de Caestecker MP. Retinoic acid signaling coordinates macrophage-dependent injury and repair after AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol 27: 495–508, 2016. doi:10.1681/ASN.2014111108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

