IRF4 haploinsufficiency in a family with Whipple's disease
- PMID: 29537367
- PMCID: PMC5915175
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.32340
IRF4 haploinsufficiency in a family with Whipple's disease
Abstract
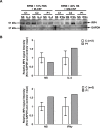
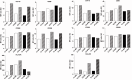
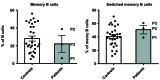
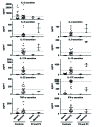
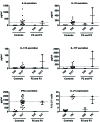
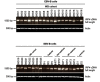
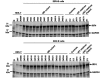
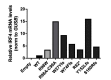
Most humans are exposed to Tropheryma whipplei (Tw). Whipple's disease (WD) strikes only a small minority of individuals infected with Tw (<0.01%), whereas asymptomatic chronic carriage is more common (<25%). We studied a multiplex kindred, containing four WD patients and five healthy Tw chronic carriers. We hypothesized that WD displays autosomal dominant (AD) inheritance, with age-dependent incomplete penetrance. We identified a single very rare non-synonymous mutation in the four patients: the private R98W variant of IRF4, a transcription factor involved in immunity. The five Tw carriers were younger, and also heterozygous for R98W. We found that R98W was loss-of-function, modified the transcriptome of heterozygous leukocytes following Tw stimulation, and was not dominant-negative. We also found that only six of the other 153 known non-synonymous IRF4 variants were loss-of-function. Finally, we found that IRF4 had evolved under purifying selection. AD IRF4 deficiency can underlie WD by haploinsufficiency, with age-dependent incomplete penetrance.
Keywords: IRF4; Whipple's disease; haploinsufficiency; human; immunology; infectious disease; inflammation; microbiology; primary immunodeficiency.
Copyright © 2018, Guérin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AG, GK, NM, JM, FF, NW, SB, DA, CM, SB, MB, VB, ED, CO, TL, LW, TN, EP, CD, RM, SB, XA, SE, SB, VR, BB, GV, FG, LQ, DC, ST, DR, LA, JB, JC No competing interests declared
Figures

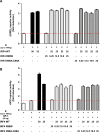
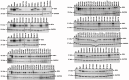

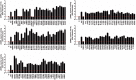
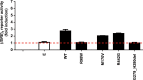
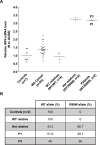
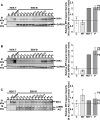
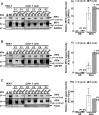

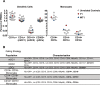


Comment in
-
Back from the brink of obscurity.Elife. 2018 Apr 18;7:e36649. doi: 10.7554/eLife.36649. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29667578 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afzali B, Grönholm J, Vandrovcova J, O'Brien C, Sun HW, Vanderleyden I, Davis FP, Khoder A, Zhang Y, Hegazy AN, Villarino AV, Palmer IW, Kaufman J, Watts NR, Kazemian M, Kamenyeva O, Keith J, Sayed A, Kasperaviciute D, Mueller M, Hughes JD, Fuss IJ, Sadiyah MF, Montgomery-Recht K, McElwee J, Restifo NP, Strober W, Linterman MA, Wingfield PT, Uhlig HH, Roychoudhuri R, Aitman TJ, Kelleher P, Lenardo MJ, O'Shea JJ, Cooper N, Laurence ADJ. BACH2 immunodeficiency illustrates an association between super-enhancers and haploinsufficiency. Nature Immunology. 2017;18:813–823. doi: 10.1038/ni.3753. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alsina L, Israelsson E, Altman MC, Dang KK, Ghandil P, Israel L, von Bernuth H, Baldwin N, Qin H, Jin Z, Banchereau R, Anguiano E, Ionan A, Abel L, Puel A, Picard C, Pascual V, Casanova JL, Chaussabel D. A narrow repertoire of transcriptional modules responsive to pyogenic bacteria is impaired in patients carrying loss-of-function mutations in MYD88 or IRAK4. Nature Immunology. 2014;15:1134–1142. doi: 10.1038/ni.3028. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andersen LL, Mørk N, Reinert LS, Kofod-Olsen E, Narita R, Jørgensen SE, Skipper KA, Höning K, Gad HH, Østergaard L, Ørntoft TF, Hornung V, Paludan SR, Mikkelsen JG, Fujita T, Christiansen M, Hartmann R, Mogensen TH. Functional IRF3 deficiency in a patient with herpes simplex encephalitis. The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 2015;212:1371–1379. doi: 10.1084/jem.20142274. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

