Effectiveness of Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion Pump Therapy During Five Years of Treatment on Metabolic Control in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 29537377
- PMCID: PMC5985384
- DOI: 10.4274/jcrpe.5117
Effectiveness of Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion Pump Therapy During Five Years of Treatment on Metabolic Control in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
Objective: To compare continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) therapy with multiple daily insulin (MDI) therapy on metabolic control in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) over the long term.
Methods: Fifty-two T1DM patients treated with CSII and monitored for at least one year prior to and at least five years following CSII were included. Thirty-eight age and sex-matched MDI controls with a 5-year follow up were recruited.
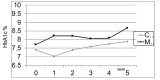
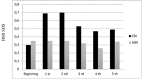
Results: Mean age of the subjects, duration of diabetes and CSII therapy were 17.0±4.8 years, 10.7±2.8 years and 7.7±1.5 years respectively. Mean hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) in the year prior to CSII, during the first year of treatment and after 5 years of CSII were 7.3±1% (56 mmol/mol), 7.0±0.7% (53 mmol/mol) and 7.8±1.3% (62 mmol/mol) respectively. Initial and 5-year mean HbA1C levels of controls were 7.9±1.08% and 8.6±1.8%. Mean HbA1c values were significantly lower in those receiving CSII therapy throughout follow-up. Basal and total insulin doses were significantly lower in the CSII group at all times. HbA1c was compared between subjects by age (0-5, 6-11 and 12-18 years) with no significant difference between them.
Conclusion: Although CSII mean HbA1c values exceeded accepted good metabolic control limits after 5 years, CSII produces better HbA1c control at all times and in all age groups compared to MDI.
Keywords: Type 1 diabetes mellitus; continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion pump therapy; multiple daily insulin therapy; HbA1c.
Figures


Similar articles
-
HbA1c variability in adults with type 1 diabetes on continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) therapy compared to multiple daily injection (MDI) treatment.BMJ Open. 2019 Dec 29;9(12):e033059. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-033059. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31888933 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of multiple daily insulin therapy with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy in adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus: a single-center experience from Turkey.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Jun;22(6):539-45. doi: 10.1515/jpem.2009.22.6.539. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2009. PMID: 19694201
-
[Metabolic control in young children with type 1 diabetes treated with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (insulin pump)].Endokrynol Diabetol Chor Przemiany Materii Wieku Rozw. 2003;9(1):11-5. Endokrynol Diabetol Chor Przemiany Materii Wieku Rozw. 2003. PMID: 12831632 Clinical Trial. Polish.
-
[An overview of so far published analyses comparating the effectiveness of the treatment with insulin pump and multiple daily injections in type 1 diabetes mellitus].Vnitr Lek. 2012 Feb;58(2):89-93. Vnitr Lek. 2012. PMID: 22463086 Review. Czech.
-
Management of diabetes mellitus: is the pump mightier than the pen?Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012 Feb 28;8(7):425-33. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2012.28. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22371161 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparing the effectiveness of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion with multiple daily insulin injection for patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus evaluated by retrospective continuous glucose monitoring: A real-world data analysis.Front Public Health. 2022 Aug 25;10:990281. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.990281. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36091534 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Choices Regarding the Administration of Insulin Among Patients With Diabetes Requiring Insulin Across Countries and Implications for Future Care.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 14;12:794363. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.794363. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35095504 Free PMC article.
-
Size matters: Influence of center size on quality of diabetes control in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes-A longitudinal analysis of the DPV cohort.Pediatr Diabetes. 2022 Feb;23(1):64-72. doi: 10.1111/pedi.13283. Epub 2021 Nov 23. Pediatr Diabetes. 2022. PMID: 34779099 Free PMC article.
-
Type 1 diabetes mellitus in children: experience in Indonesia.Clin Pediatr Endocrinol. 2021;30(1):11-18. doi: 10.1297/cpe.30.11. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Clin Pediatr Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 33446947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Long-term follow-up of efficacy of insulin pump in the treatment of children with type 1 diabetes mellitus].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2021 Feb;23(2):116-120. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2009184. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 33627203 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Misso ML, Egberts KJ, Page M, O’Connor D, Shaw J. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) versus multiple insulin injections for Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;CD005103 - PubMed
-
- Giménez M, Conget I, Jansà M, Vidal M, Chiganer G, Levy I. Efficacy of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in Type 1 diabetes: a 2-year perspective using the established criteria for funding from a National Health Service. Diabet Med. 2007;24:1419–1423. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
