Dose-response, therapeutic time-window and tPA-combinatorial efficacy of compound 21: A randomized, blinded preclinical trial in a rat model of thromboembolic stroke
- PMID: 29537907
- PMCID: PMC6681526
- DOI: 10.1177/0271678X18764773
Dose-response, therapeutic time-window and tPA-combinatorial efficacy of compound 21: A randomized, blinded preclinical trial in a rat model of thromboembolic stroke
Abstract
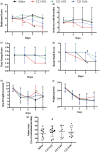
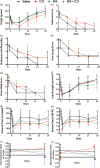
The aim of this translational, randomized, controlled, blinded preclinical trial was to determine the effect of compound 21 (C21) in embolic stroke. Rats were subjected to embolic-middle cerebral artery occlusion (eMCAO). They received C21 (0.01, 0.03 and 0.06 mg/kg/d) or saline (orally) for five days, with the first-dose given IV at 3 h post-eMCAO. For the time-window study, the optimal-dose of C21 was initiated at 3, 6 or 24 h post-eMCAO and continued for five days. For the combinatorial study, animals received IV-tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) at either 2 or 4 h, with IV-C21 (0.01 mg/kg) or saline at 3 h post-eMCAO and daily thereafter for five days. After performing the behavior tests, brains were collected for analyses. The dose-response study showed significant motor improvements with the lowest-dose (0.01 mg/kg) of C21. In the time-window study, this same dose resulted in improvements when given 6 h and 24 h post-eMCAO. Moreover, C21-treated animals performed better on the novel object recognition test. Neither the single treatment with C21 or tPA (4 h) nor the combination therapy was effective in reducing the hemorrhage or infarct size, although C21 alone lowered sensorimotor deficit scores post-eMCAO. Future studies should focus on the long-term cognitive benefits of C21, rather than acute neuroprotection.
Keywords: Compound C21; embolic middle cerebral artery occlusion; functional outcome; ischemic stroke; tissue plasminogen activator.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Opening the window: Ischemic postconditioning reduces the hyperemic response of delayed tissue plasminogen activator and extends its therapeutic time window in an embolic stroke model.Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Oct 5;764:55-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.06.043. Epub 2015 Jun 27. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26123846
-
Combination treatment with low-dose Niaspan and tissue plasminogen activator provides neuroprotection after embolic stroke in rats.J Neurol Sci. 2011 Oct 15;309(1-2):96-101. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2011.07.008. Epub 2011 Jul 29. J Neurol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21802695 Free PMC article.
-
Vepoloxamer Enhances Fibrinolysis of tPA (Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator) on Acute Ischemic Stroke.Stroke. 2019 Dec;50(12):3600-3608. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.026049. Epub 2019 Oct 7. Stroke. 2019. PMID: 31587657 Free PMC article.
-
Candesartan reduces the hemorrhage associated with delayed tissue plasminogen activator treatment in rat embolic stroke.Neurochem Res. 2013 Dec;38(12):2668-77. doi: 10.1007/s11064-013-1185-y. Epub 2013 Nov 6. Neurochem Res. 2013. PMID: 24194350 Free PMC article.
-
A novel mouse model of thromboembolic stroke.J Neurosci Methods. 2015 Dec 30;256:203-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2015.09.013. Epub 2015 Sep 18. J Neurosci Methods. 2015. PMID: 26386284 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Lipid Mediators as a Promising Therapeutic Strategy for Ischemic Stroke.Med Res Arch. 2023 Jan;11(1):10.18103/mra.v11i1.3333. doi: 10.18103/mra.v11i1.3333. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Med Res Arch. 2023. PMID: 36777192 Free PMC article.
-
TREM2 mediates physical exercise-promoted neural functional recovery in rats with ischemic stroke via microglia-promoted white matter repair.J Neuroinflammation. 2023 Feb 25;20(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02741-w. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. PMID: 36829205 Free PMC article.
-
Stimulation of angiotensin II receptor 2 preserves cognitive function and is associated with an enhanced cerebral vascular density after stroke.Vascul Pharmacol. 2021 Dec;141:106904. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2021.106904. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Vascul Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34481068 Free PMC article.
-
Compound 21, a Direct AT2R Agonist, Induces IL-10 and Inhibits Inflammation in Mice Following Traumatic Brain Injury.Neuromolecular Med. 2022 Sep;24(3):274-278. doi: 10.1007/s12017-021-08687-7. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Neuromolecular Med. 2022. PMID: 34542832 Free PMC article.
-
The counter regulatory axis of the renin angiotensin system in the brain and ischaemic stroke: Insight from preclinical stroke studies and therapeutic potential.Cell Signal. 2020 Dec;76:109809. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109809. Epub 2020 Oct 13. Cell Signal. 2020. PMID: 33059037 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Writing Group M, Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2016 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016; 133: e38–e360. - PubMed
-
- Christophe BR, Mehta SH, Garton AL, et al. Current and future perspectives on the treatment of cerebral ischemia. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2017; 18: 573–580. - PubMed
-
- Stern GM, Van Hise N, Urben LM, et al. Thrombolytic therapy in wake-up stroke patients. Clin Neuropharmacol 2017; 40: 140–146. - PubMed
-
- Savitz SI, Chopp M, Deans R, et al. Stem cell therapy as an emerging paradigm for stroke (STEPS) II. Stroke 2011; 42(3): 825–829. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

