A Randomized Phase 2 Study of ADXS11-001 Listeria monocytogenes-Listeriolysin O Immunotherapy With or Without Cisplatin in Treatment of Advanced Cervical Cancer
- PMID: 29538258
- PMCID: PMC5929492
- DOI: 10.1097/IGC.0000000000001235
A Randomized Phase 2 Study of ADXS11-001 Listeria monocytogenes-Listeriolysin O Immunotherapy With or Without Cisplatin in Treatment of Advanced Cervical Cancer
Abstract
Objectives: A global unmet medical need exists for effective treatments for persistent, recurrent, or metastatic cervical cancer, as patients have a short life expectancy. Recently, immunotherapies have shown promising survival benefits for patients with advanced forms of cancer. Axalimogene filolisbac (ADXS11-001), a Listeria monocytogenes immunotherapy with a broad effect on the immune system, is under investigation for treatment of human papillomavirus-associated cancers including cervical cancer.
Methods: This phase 2 study evaluated the safety and efficacy of ADXS11-001, administered with or without cisplatin, in patients with recurrent/refractory cervical cancer following prior chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy. A total of 109 patients were treated, and 69 were evaluable for tumor response at equal to or more than 3 months postbaseline.
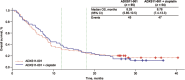
Results: Median overall survival (OS) was comparable between treatment groups (ADXS11-001: 8.28 months; 95% confidence interval [CI], 5.85-10.5 months; ADXS11-001 + cisplatin: 8.78 months; 95% CI, 7.4-13.3 months). The 12- and 18-month milestone OS rates were 30.9% versus 38.9%, and 23.6% versus 25.9% for each group, respectively (34.9% and 24.8% combined). Median progression-free survival (6.10 vs 6.08 months) and the overall response rate (17.1% vs 14.7%) were similar for both groups. ADXS11-001 was generally well tolerated; adverse events were predominantly mild to moderate in severity and not related to treatment. More adverse events were reported in the combination group (429 vs 275).
Conclusions: These promising safety and efficacy results, including the encouraging 12-month 34.9% combined OS rate, warrant further investigation of ADXS11-001 for treatment of recurrent/refractory cervical cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
P.B. has received research funding from Advaxis, Inc, while working for Chittaranjan National Cancer Institute; S.G. has received research funding from Sanofi-Aventis; R.P. is employed by and owns stock from Advaxis, Inc. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. International Agency for Research on Cancer. In: Latest World Cancer Statistics. Global Cancer Burden Rises to 14.1 Million New Cases in 2012: Marked Increase in Breast Cancers Must Be Addressed [press release]. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2013.
-
- Bruni L, Barrionuevo-Rosas L, Albero G, et al. Human Papillomavirus and Related Diseases in the World. Summary Report. Barcelona, Spain: ICO Information Centre on HPV and Cancer (HPV Information Centre); 2017.
-
- World Health Organization/Institut Català d'Oncologia Information Centre on HPV and Cervical Cancer (HPV Information Centre). Human Papillomavirus and Related Cancers. Summary Report Update. Barcelona, Spain: WHO/ICO HPV Information Centre; 2010.
-
- Clifford GM, Rana RK, Franceschi S, et al. Human papillomavirus genotype distribution in low-grade cervical lesions: comparison by geographic region and with cervical cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2005;14:1157–1164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical