Role of Disputed Mutations in the rpoB Gene in Interpretation of Automated Liquid MGIT Culture Results for Rifampin Susceptibility Testing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- PMID: 29540456
- PMCID: PMC5925711
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01599-17
Role of Disputed Mutations in the rpoB Gene in Interpretation of Automated Liquid MGIT Culture Results for Rifampin Susceptibility Testing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Abstract
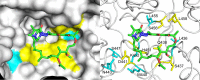
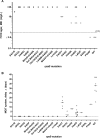
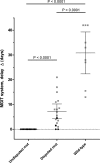
Low-level rifampin resistance associated with specific rpoB mutations (referred as "disputed") in Mycobacterium tuberculosis is easily missed by some phenotypic methods. To understand the mechanism by which some mutations are systematically missed by MGIT phenotypic testing, we performed an in silico analysis of their effect on the structural interaction between the RpoB protein and rifampin. We also characterized 24 representative clinical isolates by determining MICs on 7H10 agar and testing them by an extended MGIT protocol. We analyzed 2,097 line probe assays, and 156 (7.4%) cases showed a hybridization pattern referred to here as "no wild type + no mutation." Isolates harboring "disputed" mutations (L430P, D435Y, H445C/L/N/S, and L452P) tested susceptible in MGIT, with prevalence ranging from 15 to 57% (overall, 16 out of 55 isolates [29%]). Our in silico analysis did not highlight any difference between "disputed" and "undisputed" substitutions, indicating that all rpoB missense mutations affect the rifampin binding site. MIC testing showed that "undisputed" mutations are associated with higher MIC values (≥20 mg/liter) compared to "disputed" mutations (4 to >20 mg/liter). Whereas "undisputed" mutations didn't show any delay (Δ) in time to positivity of the test tube compared to the control tube on extended MGIT protocol, "disputed" mutations showed a mean Δ of 7.2 days (95% confidence interval [CI], 4.2 to 10.2 days; P < 0.05), providing evidence that mutations conferring low-level resistance are associated with a delay in growth on MGIT. Considering the proved relevance of L430P, D435Y, H445C/L/N, and L452P mutations in determining clinical resistance, genotypic drug susceptibility testing (DST) should be used to replace phenotypic results (MGIT) when such mutations are found.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; diagnostics; drug susceptibility testing; multidrug resistance.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reevaluating Rifampicin Breakpoint Concentrations for Mycobacterium tuberculosis Isolates with Disputed rpoB Mutations and Discordant Susceptibility Phenotypes.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0208721. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02087-21. Epub 2022 Feb 2. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35107324 Free PMC article.
-
Occurrence of disputed rpoB mutations among Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates phenotypically susceptible to rifampicin in a country with a low incidence of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis.BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Jan 3;19(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-3638-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30606116 Free PMC article.
-
Variable ability of rapid tests to detect Mycobacterium tuberculosis rpoB mutations conferring phenotypically occult rifampicin resistance.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 14;9(1):11826. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48401-z. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31413308 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the rifampicin resistance mutations and rifabutin susceptibility in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: A meta-analysis.J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2025 Jan;40:53-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2024.11.014. Epub 2024 Nov 29. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2025. PMID: 39617268 Review.
-
Mutations inside rifampicin-resistance determining region of rpoB gene associated with rifampicin-resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.J Infect Public Health. 2018 Sep-Oct;11(5):605-610. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2018.04.005. Epub 2018 Apr 26. J Infect Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29706316 Review.
Cited by
-
Minimum inhibitory concentrations of rifampin and isoniazid among multidrug and isoniazid resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Ethiopia.PLoS One. 2022 Sep 13;17(9):e0274426. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0274426. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36099255 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic epidemiology of tuberculosis in eastern Malaysia: insights for strengthening public health responses.Microb Genom. 2021 May;7(5):000573. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000573. Microb Genom. 2021. PMID: 33945455 Free PMC article.
-
Cryptic Resistance Mutations Associated With Misdiagnoses of Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis.J Infect Dis. 2019 Jun 19;220(2):316-320. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiz104. J Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30875421 Free PMC article.
-
rpoB Mutations and Effects on Rifampin Resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Infect Drug Resist. 2021 Oct 5;14:4119-4128. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S333433. eCollection 2021. Infect Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 34675557 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and genetic basis of first-line drug resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Ca Mau, Vietnam.ERJ Open Res. 2022 Oct 24;8(4):00122-2022. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00122-2022. eCollection 2022 Oct. ERJ Open Res. 2022. PMID: 36299370 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. 2008. WHO policy statement: molecular line probe assays for rapid screening of patients at risk of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland.
-
- World Health Organization. 2013. Xpert MTB/RIF assay for the diagnosis of pulmonary and extrapulmonary TB in adults and children—policy update. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. 2017. WHO Meeting Report of a Technical Expert Consultation: non-inferiority analysis of Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra compared to Xpert MTB/RIF. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

