The mir-279/996 cluster represses receptor tyrosine kinase signaling to determine cell fates in the Drosophila eye
- PMID: 29540498
- PMCID: PMC5963866
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.159053
The mir-279/996 cluster represses receptor tyrosine kinase signaling to determine cell fates in the Drosophila eye
Abstract
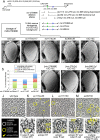
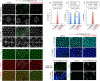
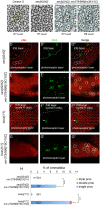
Photoreceptors in the crystalline Drosophila eye are recruited by receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)/Ras signaling mediated by Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and the Sevenless (Sev) receptor. Analyses of an allelic deletion series of the mir-279/996 locus, along with a panel of modified genomic rescue transgenes, show that Drosophila eye patterning depends on both miRNAs. Transcriptional reporter and activity sensor transgenes reveal expression and function of miR-279/996 in non-neural cells of the developing eye. Moreover, mir-279/996 mutants exhibit substantial numbers of ectopic photoreceptors, particularly of R7, and cone cell loss. These miRNAs restrict RTK signaling in the eye, since mir-279/996 nulls are dominantly suppressed by positive components of the EGFR pathway and enhanced by heterozygosity for an EGFR repressor. miR-279/996 limit photoreceptor recruitment by targeting multiple positive RTK/Ras signaling components that promote photoreceptor/R7 specification. Strikingly, deletion of mir-279/996 sufficiently derepresses RTK/Ras signaling so as to rescue a population of R7 cells in R7-specific RTK null mutants boss and sev, which otherwise completely lack this cell fate. Altogether, we reveal a rare setting of developmental cell specification that involves substantial miRNA control.
Keywords: Drosophila; MicroRNA; R7 photoreceptor; RTK signaling.
© 2018. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The role of Sevenless in Drosophila R7 photoreceptor specification.Dev Biol. 2019 Oct 15;454(2):181-189. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2019.06.007. Epub 2019 Jun 14. Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31207209 Free PMC article.
-
Three distinct roles for notch in Drosophila R7 photoreceptor specification.PLoS Biol. 2011 Aug;9(8):e1001132. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001132. Epub 2011 Aug 23. PLoS Biol. 2011. PMID: 21886484 Free PMC article.
-
Apical accumulation of the Sevenless receptor tyrosine kinase during Drosophila eye development is promoted by the small GTPase Rap1.Genetics. 2014 Aug;197(4):1237-50. doi: 10.1534/genetics.114.166272. Epub 2014 Jun 3. Genetics. 2014. PMID: 24899161 Free PMC article.
-
Stop and go: antagonistic signals in the specification of the Drosophila R7 photoreceptor viewed from an evolutionary perspective.Fly (Austin). 2012 Oct-Dec;6(4):228-33. doi: 10.4161/fly.21102. Epub 2012 Aug 10. Fly (Austin). 2012. PMID: 22878552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic analysis of the sevenless signal transduction pathway of Drosophila.Dev Suppl. 1993:41-6. Dev Suppl. 1993. PMID: 8049486 Review.
Cited by
-
Satellite-Like W-Elements: Repetitive, Transcribed, and Putative Mobile Genetic Factors with Potential Roles for Biology and Evolution of Schistosoma mansoni.Genome Biol Evol. 2021 Oct 1;13(10):evab204. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evab204. Genome Biol Evol. 2021. PMID: 34469545 Free PMC article.
-
Sperm fate is promoted by the mir-44 microRNA family in the Caenorhabditis elegans hermaphrodite germline.Genetics. 2021 Mar 3;217(1):1-14. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyaa006. Genetics. 2021. PMID: 33683352 Free PMC article.
-
A nonneural miRNA cluster mediates hearing via repression of two neural targets.Genes Dev. 2023 Dec 26;37(21-24):1041-1051. doi: 10.1101/gad.351052.123. Genes Dev. 2023. PMID: 38110249 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo AGO-APP identifies a module of microRNAs cooperatively preserving neural progenitors.PLoS Genet. 2025 Apr 29;21(4):e1011680. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011680. eCollection 2025 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2025. PMID: 40299997 Free PMC article.
-
The Biological Roles of microRNAs in Drosophila Development.Insects. 2024 Jun 30;15(7):491. doi: 10.3390/insects15070491. Insects. 2024. PMID: 39057224 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

