A microtubule-dynein tethering complex regulates the axonemal inner dynein f (I1)
- PMID: 29540525
- PMCID: PMC5921573
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E17-11-0689
A microtubule-dynein tethering complex regulates the axonemal inner dynein f (I1)
Abstract
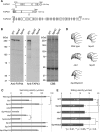
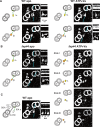
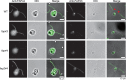
Motility of cilia/flagella is generated by a coordinated activity of thousands of dyneins. Inner dynein arms (IDAs) are particularly important for the formation of ciliary/flagellar waveforms, but the molecular mechanism of IDA regulation is poorly understood. Here we show using cryoelectron tomography and biochemical analyses of Chlamydomonas flagella that a conserved protein FAP44 forms a complex that tethers IDA f (I1 dynein) head domains to the A-tubule of the axonemal outer doublet microtubule. In wild-type flagella, IDA f showed little nucleotide-dependent movement except for a tilt in the f β head perpendicular to the microtubule-sliding direction. In the absence of the tether complex, however, addition of ATP and vanadate caused a large conformational change in the IDA f head domains, suggesting that the movement of IDA f is mechanically restricted by the tether complex. Motility defects in flagella missing the tether demonstrates the importance of the IDA f-tether interaction in the regulation of ciliary/flagellar beating.
Figures



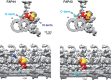
Similar articles
-
The I1 dynein-associated tether and tether head complex is a conserved regulator of ciliary motility.Mol Biol Cell. 2018 May 1;29(9):1048-1059. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E18-02-0142. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Mol Biol Cell. 2018. PMID: 29514928 Free PMC article.
-
Composition and function of ciliary inner-dynein-arm subunits studied in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2021 Mar;78(3):77-96. doi: 10.1002/cm.21662. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2021. PMID: 33876572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure of a microtubule-bound axonemal dynein.Nat Commun. 2021 Jan 20;12(1):477. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20735-7. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33473120 Free PMC article.
-
Chlamydomonas IC97, an intermediate chain of the flagellar dynein f/I1, is required for normal flagellar and cellular motility.mSphere. 2024 Dec 19;9(12):e0055824. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00558-24. Epub 2024 Nov 27. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 39601552 Free PMC article.
-
Functional diversity of axonemal dyneins as assessed by in vitro and in vivo motility assays of Chlamydomonas mutants.Zoolog Sci. 2014 Oct;31(10):633-44. doi: 10.2108/zs140066. Zoolog Sci. 2014. PMID: 25284382 Review.
Cited by
-
Ccdc113/Ccdc96 complex, a novel regulator of ciliary beating that connects radial spoke 3 to dynein g and the nexin link.PLoS Genet. 2021 Mar 4;17(3):e1009388. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009388. eCollection 2021 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 33661892 Free PMC article.
-
Nexin-Dynein regulatory complex component DRC7 but not FBXL13 is required for sperm flagellum formation and male fertility in mice.PLoS Genet. 2020 Jan 21;16(1):e1008585. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008585. eCollection 2020 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 31961863 Free PMC article.
-
Intraflagellar transport trains and motors: Insights from structure.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Nov;107:82-90. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.05.021. Epub 2020 Jul 16. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32684327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure of the Decorated Ciliary Doublet Microtubule.Cell. 2019 Oct 31;179(4):909-922.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.09.030. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Cell. 2019. PMID: 31668805 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic causes of male infertility: snapshot on morphological abnormalities of the sperm flagellum.Basic Clin Androl. 2019 Mar 4;29:2. doi: 10.1186/s12610-019-0083-9. eCollection 2019. Basic Clin Androl. 2019. PMID: 30867909 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

