Control of insulin granule formation and function by the ABC transporters ABCG1 and ABCA1 and by oxysterol binding protein OSBP
- PMID: 29540530
- PMCID: PMC5935073
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E17-08-0519
Control of insulin granule formation and function by the ABC transporters ABCG1 and ABCA1 and by oxysterol binding protein OSBP
Abstract
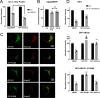
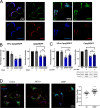
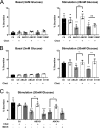
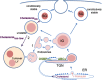
In pancreatic β-cells, insulin granule membranes are enriched in cholesterol and are both recycled and newly generated. Cholesterol's role in supporting granule membrane formation and function is poorly understood. ATP binding cassette transporters ABCG1 and ABCA1 regulate intracellular cholesterol and are important for insulin secretion. RNAi inter-ference-induced depletion in cultured pancreatic β-cells shows that ABCG1 is needed to stabilize newly made insulin granules against lysosomal degradation; ABCA1 is also involved but to a lesser extent. Both transporters are also required for optimum glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, likely via complementary roles. Exogenous cholesterol addition rescues knockdown-induced granule loss (ABCG1) and reduced secretion (both transporters). Another cholesterol transport protein, oxysterol binding protein (OSBP), appears to act proximally as a source of endogenous cholesterol for granule formation. Its knockdown caused similar defective stability of young granules and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, neither of which were rescued with exogenous cholesterol. Dual knockdowns of OSBP and ABC transporters support their serial function in supplying and concentrating cholesterol for granule formation. OSBP knockdown also decreased proinsulin synthesis consistent with a proximal endoplasmic reticulum defect. Thus, membrane cholesterol distribution contributes to insulin homeostasis at production, packaging, and export levels through the actions of OSBP and ABCs G1 and A1.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Reinterpretation of the localization of the ATP binding cassette transporter ABCG1 in insulin-secreting cells and insights regarding its trafficking and function.PLoS One. 2018 Sep 20;13(9):e0198383. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198383. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30235209 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein A-I improves pancreatic β-cell function independent of the ATP-binding cassette transporters ABCA1 and ABCG1.FASEB J. 2019 Jul;33(7):8479-8489. doi: 10.1096/fj.201802512RR. Epub 2019 Apr 10. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30970222
-
Cadmium induced redistribution of cholesterol by upregulating ABCA1 and downregulating OSBP.J Inorg Biochem. 2018 Dec;189:199-207. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2018.09.016. Epub 2018 Sep 29. J Inorg Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30317066
-
Caveolin-1 and ATP binding cassette transporter A1 and G1-mediated cholesterol efflux.Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2014;14(2):142-8. doi: 10.2174/1871529x14666140505122802. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2014. PMID: 24801727 Review.
-
ATP-binding cassette transporters A1 and G1, HDL metabolism, cholesterol efflux, and inflammation: important targets for the treatment of atherosclerosis.Curr Drug Targets. 2011 May;12(5):647-60. doi: 10.2174/138945011795378522. Curr Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21039336 Review.
Cited by
-
Cholesterol Redistribution in Pancreatic β-Cells: A Flexible Path to Regulate Insulin Secretion.Biomolecules. 2023 Jan 24;13(2):224. doi: 10.3390/biom13020224. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36830593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reinterpretation of the localization of the ATP binding cassette transporter ABCG1 in insulin-secreting cells and insights regarding its trafficking and function.PLoS One. 2018 Sep 20;13(9):e0198383. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198383. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30235209 Free PMC article.
-
Normal and defective pathways in biogenesis and maintenance of the insulin storage pool.J Clin Invest. 2021 Jan 19;131(2):e142240. doi: 10.1172/JCI142240. J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 33463547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin granule biogenesis and exocytosis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Mar;78(5):1957-1970. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03688-4. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33146746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The PI(4)P phosphatase Sac2 controls insulin granule docking and release.J Cell Biol. 2019 Nov 4;218(11):3714-3729. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201903121. Epub 2019 Sep 18. J Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31533953 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balch WE, Rothman JE. (1985). Characterization of protein transport between successive compartments of the Golgi apparatus: asymmetric properties of donor and acceptor activities in a cell-free system. Arch Biochem Biophys , 413–425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

