Intracellular Nucleic Acid Sensing Triggers Necroptosis through Synergistic Type I IFN and TNF Signaling
- PMID: 29540580
- PMCID: PMC5893403
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1701492
Intracellular Nucleic Acid Sensing Triggers Necroptosis through Synergistic Type I IFN and TNF Signaling
Abstract
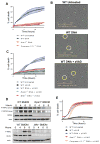
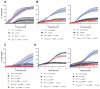
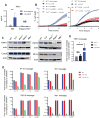
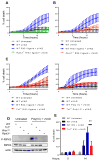
The sensing of viral nucleic acids within the cytosol is essential for the induction of innate immune responses following infection. However, this sensing occurs within cells that have already been infected. The death of infected cells can be beneficial to the host by eliminating the virus's replicative niche and facilitating the release of inflammatory mediators. In this study, we show that sensing of intracellular DNA or RNA by cGAS-STING or RIG-I-MAVS, respectively, leads to activation of RIPK3 and necroptosis in bone marrow-derived macrophages. Notably, this requires signaling through both type I IFN and TNF receptors, revealing synergy between these pathways to induce cell death. Furthermore, we show that hyperactivation of STING in mice leads to a shock-like phenotype, the mortality of which requires activation of the necroptotic pathway and IFN and TNF cosignaling, demonstrating that necroptosis is one outcome of STING signaling in vivo.
Copyright © 2018 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Nogusa S, Thapa RJ, Dillon CP, Liedmann S, Oguin TH, Ingram JP, Rodriguez DA, Kosoff R, Sharma S, Sturm O, Verbist K, Gough PJ, Bertin J, Hartmann BM, Sealfon SC, Kaiser WJ, Mocarski ES, López CB, Thomas PG, Oberst A, Green DR, Balachandran S. RIPK3 Activates Parallel Pathways of MLKL-Driven Necroptosis and FADD-Mediated Apoptosis to Protect against Influenza A Virus. Cell Host and Microbe. 2016;20:13–24. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huang Z, Wu SQ, Liang Y, Zhou X, Chen W, Li L, Wu J, Zhuang Q, Chen C, Li J, Zhong CQ, Xia W, Zhou R, Zheng C, Han J. RIP1/RIP3 binding to HSV-1 ICP6 initiates necroptosis to restrict virus propagation in mice. Cell Host and Microbe. 2015;17:229–242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

