ALY RNA-Binding Proteins Are Required for Nucleocytosolic mRNA Transport and Modulate Plant Growth and Development
- PMID: 29540591
- PMCID: PMC5933122
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.18.00173
ALY RNA-Binding Proteins Are Required for Nucleocytosolic mRNA Transport and Modulate Plant Growth and Development
Abstract
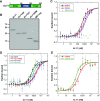
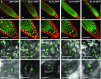
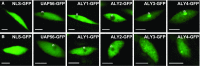
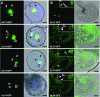
The regulated transport of mRNAs from the cell nucleus to the cytosol is a critical step linking transcript synthesis and processing with translation. However, in plants, only a few of the factors that act in the mRNA export pathway have been functionally characterized. Flowering plant genomes encode several members of the ALY protein family, which function as mRNA export factors in other organisms. Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) ALY1 to ALY4 are commonly detected in root and leaf cells, but they are differentially expressed in reproductive tissue. Moreover, the subnuclear distribution of ALY1/2 differs from that of ALY3/4. ALY1 binds with higher affinity to single-stranded RNA than double-stranded RNA and single-stranded DNA and interacts preferentially with 5-methylcytosine-modified single-stranded RNA. Compared with the full-length protein, the individual RNA recognition motif of ALY1 binds RNA only weakly. ALY proteins interact with the RNA helicase UAP56, indicating a link to the mRNA export machinery. Consistently, ALY1 complements the lethal phenotype of yeast cells lacking the ALY1 ortholog Yra1. Whereas individual aly mutants have a wild-type appearance, disruption of ALY1 to ALY4 in 4xaly plants causes vegetative and reproductive defects, including strongly reduced growth, altered flower morphology, as well as abnormal ovules and female gametophytes, causing reduced seed production. Moreover, polyadenylated mRNAs accumulate in the nuclei of 4xaly cells. Our results highlight the requirement of efficient mRNA nucleocytosolic transport for proper plant growth and development and indicate that ALY1 to ALY4 act partly redundantly in this process; however, differences in expression and subnuclear localization suggest distinct functions.
© 2018 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Antosch M, Schubert V, Holzinger P, Houben A, Grasser KD (2015) Mitotic lifecycle of chromosomal 3xHMG-box proteins and the role of their N-terminal domain in the association with rDNA loci and proteolysis. New Phytol 208: 1067–1077 - PubMed
-
- Antosz W, Pfab A, Ehrnsberger HF, Holzinger P, Köllen K, Mortensen SA, Bruckmann A, Schubert T, Längst G, Griesenbeck J, et al. (2017) The composition of the Arabidopsis RNA polymerase II transcript elongation complex reveals the interplay between elongation and mRNA processing factors. Plant Cell 29: 854–870 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bruhn L, Munnerlyn A, Grosschedl R (1997) ALY, a context-dependent coactivator of LEF-1 and AML-1, is required for TCRalpha enhancer function. Genes Dev 11: 640–653 - PubMed
-
- Burd CG, Dreyfuss G (1994) Conserved structures and diversity of functions of RNA-binding proteins. Science 265: 615–621 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

