β-Adrenoceptor subtypes and cAMP role in adrenaline- and noradrenaline-induced relaxation in the rat thoracic aorta
- PMID: 29540622
- PMCID: PMC5863045
- DOI: 10.1540/jsmr.54.1
β-Adrenoceptor subtypes and cAMP role in adrenaline- and noradrenaline-induced relaxation in the rat thoracic aorta
Abstract
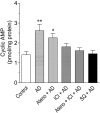
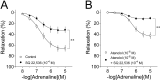
Object We identified the β-adrenoceptor (β-AR) subtypes responsible for the relaxant responses to adrenaline (AD) and noradrenaline (NA) in the rat thoracic aorta and examined the role of cAMP which is involved in these relaxant responses. Methods The effects of β-AR antagonists or the adenylyl cyclase inhibitor SQ 22,536 on AD- and NA-induced relaxant responses in phenylephrine-induced contraction and increases in cAMP levels were examined in isolated, endothelium-denuded rat thoracic aorta segments. Results AD-induced relaxation was completely suppressed by propranolol (10-7 M) or by ICI-118,551 (10-8 M) plus atenolol (10-6 M), and was also very strongly inhibited by ICI-118,551 (10-8 M) alone. AD (10-5 M) increased tissue cAMP levels by approximately 1.9-fold compared with that in non-stimulated aortic tissue, but did not significantly increase cAMP levels in the presence of ICI-118,551 (10-8 M) or SQ 22,536 (10-4 M). AD-induced relaxation was strongly suppressed by SQ 22,536 (10-4 M). NA-induced relaxation was almost completely suppressed by atenolol (10-6 M) plus ICI-118,551 (10-8 M) although it was hardly affected by ICI-118,551 (10-8 M) alone. NA (10-5 M) increased tissue cAMP levels by approximately 2.2-fold compared with that in non-stimulated aortic tissue, but did not significantly increase cAMP levels in the presence of atenolol (10-6 M) or SQ 22,536 (10-4 M). NA-induced relaxation was strongly suppressed by SQ 22,536 (10-4 M). Conclusion In rat thoracic aorta, AD- and NA-induced relaxations, which are both strongly dependent on increased tissue cAMP levels, are mainly mediated through β2- and β1-adrenoceptors respectively.
Keywords: catecholamines; rat thoracic aorta; relaxation; tissue cyclic AMP level; β-adrenoceptor (β-AR).
Figures




Similar articles
-
Pharmacological identification of β-adrenoceptor subtypes mediating isoprenaline-induced relaxation of guinea pig colonic longitudinal smooth muscle.J Smooth Muscle Res. 2018;54(0):13-27. doi: 10.1540/jsmr.54.13. J Smooth Muscle Res. 2018. PMID: 29540623 Free PMC article.
-
Beta 1-, beta 2- and atypical beta-adrenoceptor-mediated relaxation in rat isolated aorta.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Feb;129(4):637-44. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703091. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10683187 Free PMC article.
-
Studies on the mechanisms underlying beta-adrenoceptor-mediated relaxation of rat abdominal aorta.J Smooth Muscle Res. 2006 Dec;42(6):217-25. doi: 10.1540/jsmr.42.217. J Smooth Muscle Res. 2006. PMID: 17435380
-
Novel signal transduction pathway mediating endothelium-dependent beta-adrenoceptor vasorelaxation in rat thoracic aorta.Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Nov;107(3):684-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14507.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1992. PMID: 1335334 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of adrenergic mechanisms for the stress-induced breast cancer carcinogenesis.J Cell Physiol. 2022 Apr;237(4):2107-2127. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30707. Epub 2022 Mar 3. J Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35243626 Review.
Cited by
-
Sympathetic Nervous System and Atherosclerosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 23;24(17):13132. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713132. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37685939 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nagatomo T, Koike K. Recent advances in structure, binding sites with ligands and pharmacological function of β-adrenoceptors obtained by molecular biology and molecular modeling. Life Sci. 2000; 66(25): 2419–26. - PubMed
-
- Tank AW, Lee Wong D. Peripheral and central effects of circulating catecholamines. Compr Physiol. 2015; 5(1): 1–15. - PubMed
-
- Lands AM, Arnold A, McAuliff JP, Luduena FP, Brown TG. Differentiation of receptor systems activated by sympathomimetic amines. Nature. 1967; 214(5088): 597–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

