The effects of saline water consumption on the ultrasonographic and histopathological appearance of the kidney and liver in Barki sheep
- PMID: 29540632
- PMCID: PMC5989016
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.17-0596
The effects of saline water consumption on the ultrasonographic and histopathological appearance of the kidney and liver in Barki sheep
Abstract
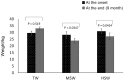
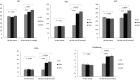
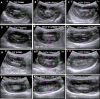
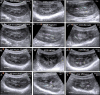
The objective of this study was to evaluate the impact of varying degrees of water salinity on the ultrasonographical and histopathological appearance of the liver and kidneys in Barki sheep. Thirty Barki sheep (initial weight, 29.48 ± 0.81 kg) were allocated into three groups (n=10 per group) based on the type of drinking water for 9 months: the tap water (TW) group (350 ppm total dissolved solids [TDS]); the moderate saline water (MSW) group (4,557 ppm TDS); and the high saline water (HSW) group (8,934 ppm TDS). After 9 months, the body weight was significantly decreased in sheep subjected to MSW (P=0.0347) and HSW (P=0.0424). Alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, urea, and creatinine were significantly increased (P<0.05) in sheep subjected to MSW and HSW. Ultrasonographic examination of the right and left kidneys revealed an increased length of both kidneys with crystal formation, particularly in male sheep. Ultrasonographic examination of the liver showed hyperechogenic dots varying in size and number between males and females. Histopathological examination of kidney revealed significant changes in both MSW and HSW groups such as hyaline matrix formation, atrophied glomerular tufts, and intramedullary congestion. Histopathological examination of the liver revealed slight fatty liver changes, slight fibrosis around the bile duct, massive inflammatory cell infiltration and vacuolar changes of hepatocytes in both MSW and HSW groups. In conclusion, water salinity negatively affects the body weight, liver and kidney appearance of Barki sheep and thus sheep production.
Keywords: histopathology; kidney; liver; sheep; ultrasonography.
Figures
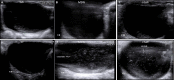
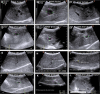
References
-
- Assad F., El-Sherif M. A.2002. Effect of drinking saline water and feed shortage on adaptive responses of sheep and camels. Small Rumin. Res. 45: 279–290. doi: 10.1016/S0921-4488(02)00083-4 - DOI
-
- Attia-Ismail S. A., Abdo A. R., Asker A. R. T.2008. Effect of salinity level in drinking water on feed intake, nutrient utilization, water intake and turnover and rumen function in sheep and goats. Egypt. J. Sheep Goats Sci. 3: 77–94.
-
- Bancroft J. D., Gamble M.2008. Theory and practice of histological techniques book. Churchill Livingstone, New York /Elsevier.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

