Erasmus Syndrome: Silicosis and Systemic Sclerosis
- PMID: 29540971
- PMCID: PMC5844136
- DOI: 10.4103/ijoem.IJOEM_120_17
Erasmus Syndrome: Silicosis and Systemic Sclerosis
Abstract
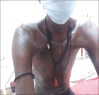
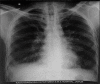
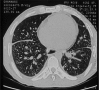
Several occupational hazards, especially exposure to silica, have been implicated as causal factors for the development of scleroderma-like disorders. Compared to other connective tissue disorders, silica-associated systemic sclerosis (SA-SS) is relatively rare. Silica-induced scleroderma is indistinguishable from idiopathic systemic sclerosis. However, the former expresses a high predisposition of pulmonary involvement and anti-Scl-70 antibody. We report the case of a 42-year-old male, stone cutter by occupation, who was diagnosed as simple chronic silicosis and developed systemic sclerosis.
Keywords: Chronic silicosis; scleroderma; systemic sclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bramwell B. Diffuse scleroderma: Its frequency; its occurrence in stonemasons. Edinburgh Med J. 1914;12:387–401.
-
- Erasmus LD. Scleroderma in Gold-Miners on the Witwatersrand with Particular Reference to Pulmonary Manifestations. S Afr J Lab Clin Med. 1957;3:209–31. - PubMed
-
- Rodnan GP, Benedek TG, Medsger TA, Jr, Cammarata RJ. The association of progressive systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) with coal miners' pneumoconiosis and other forms of silicosis. Ann Intern Med. 1967;66:323–34. - PubMed
-
- Devulder B, Plouvier B, Martin JC, Lenoir L. The association: Scleroderma-silicosis or Erasmus' syndrome (author's transl) Nouv Presse Med. 1977;6:2877–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

