Transcription Factor KLF10 Constrains IL-17-Committed Vγ4+ γδ T Cells
- PMID: 29541070
- PMCID: PMC5835516
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00196
Transcription Factor KLF10 Constrains IL-17-Committed Vγ4+ γδ T Cells
Abstract
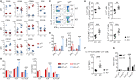
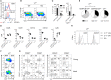
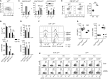
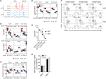
γδ T cells, known to be an important source of innate IL-17 in mice, provide critical contributions to host immune responses. Development and function of γδ T cells are directed by networks of diverse transcription factors (TFs). Here, we examine the role of the zinc finger TFs, Kruppel-like factor 10 (KLF10), in the regulation of IL-17-committed CD27- γδ T (γδ27--17) cells. We found selective augmentation of Vγ4+ γδ27- cells with higher IL-17 production in KLF10-deficient mice. Surprisingly, KLF10-deficient CD127hi Vγ4+ γδ27--17 cells expressed higher levels of CD5 than their wild-type counterparts, with hyper-responsiveness to cytokine, but not T-cell receptor, stimuli. Thymic maturation of Vγ4+ γδ27- cells was enhanced in newborn mice deficient in KLF10. Finally, a mixed bone marrow chimera study indicates that intrinsic KLF10 signaling is requisite to limit Vγ4+ γδ27--17 cells. Collectively, these findings demonstrate that KLF10 regulates thymic development of Vγ4+ γδ27- cells and their peripheral homeostasis at steady state.
Keywords: IL-17; Innate-like γδ-17; KLF10; homeostasis; γδ T cells.
Figures




References
-
- Venuprasad K, Huang H, Harada Y, Elly C, Subramaniam M, Spelsberg T, et al. The E3 ubiquitin ligase Itch regulates expression of transcription factor Foxp3 and airway inflammation by enhancing the function of transcription factor TIEG1. Nat Immunol (2008) 9(3):245–53.10.1038/ni1564 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

