Maximal repetition performance, rating of perceived exertion, and muscle fatigue during paired set training performed with different rest intervals
- PMID: 29541107
- PMCID: PMC5812862
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jesf.2015.08.002
Maximal repetition performance, rating of perceived exertion, and muscle fatigue during paired set training performed with different rest intervals
Abstract
Background/objective: The purpose of this study was to examine rest interval length between agonist-antagonist paired set training (PS) on maximal repetition performance, rating of perceived exertion, and neuromuscular fatigue.
Methods: Fourteen trained men (age, 24.2 ± 1.1 years; height, 175 ± 5.5 cm; body mass, 76.6 ± 7.0 kg) performed two experimental protocols in random order with 2 minutes (P2) or 4 minutes (P4) between agonist-antagonist PS, which consisted of a bench press set followed immediately by a seated row set with 8-repetition maximum loads, respectively. A total of three PS were performed for each rest interval protocol. The total repetitions performed and the rating of perceived exertion were recorded for each exercise set within each rest interval protocol. Electromyography signals were recorded for the posterior deltoid, biceps brachii, pectoralis major, and triceps brachii muscles during the SR exercise. The electromyography signals were then used to calculate a fatigue index for each rest interval protocol.
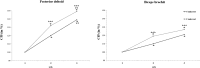
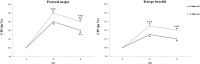
Results: No significant differences were identified in the total repetitions completed between rest interval protocols for the bench press (P2 = 22.9 ± 1.3 and P4 = 22.6 ± 0.8) and seated row (P2 = 25.4 ± 1.7 and P4 = 25.1 ± 1.3). However, a significantly higher fatigue index was found for all muscles under the P2 versus the P4 protocol.
Conclusion: When performing agonist-antagonist PS, prescribing a shorter rest interval between PS may induce higher levels of fatigue, albeit with similar total repetitions versus a longer rest interval.
Keywords: Electromyography; Exercise; Recovery; Resistance training.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Volume Load and Neuromuscular Fatigue During an Acute Bout of Agonist-Antagonist Paired-Set vs. Traditional-Set Training.J Strength Cond Res. 2017 Oct;31(10):2777-2784. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001059. J Strength Cond Res. 2017. PMID: 28933712 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of rest interval array on training volume, perceived exertion, neuromuscular fatigue, and metabolic responses during agonist-antagonist muscle alternative training.J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2020 Apr;60(4):536-543. doi: 10.23736/S0022-4707.19.10365-9. Epub 2020 Jan 23. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2020. PMID: 31974337
-
Acute Hormone Responses Subsequent to Agonist-Antagonist Paired Set vs. Traditional Straight Set Resistance Training.J Strength Cond Res. 2020 Jun;34(6):1591-1599. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000002633. J Strength Cond Res. 2020. PMID: 29979283 Clinical Trial.
-
Maximal strength performance, efficiency, and myoelectric responses with differing intra-set rest intervals during paired set training.J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2020 Jan;24(1):263-268. doi: 10.1016/j.jbmt.2019.06.003. Epub 2019 Jun 4. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2020. PMID: 31987555 Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of rest interval length manipulation of the first upper-body resistance exercise in sequence on acute performance of subsequent exercises in men and women.J Strength Cond Res. 2012 Nov;26(11):2929-38. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e318270fcf0. J Strength Cond Res. 2012. PMID: 22964859 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Acute Effects of a Percussive Massage Treatment on Movement Velocity during Resistance Training.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jul 21;18(15):7726. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18157726. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34360032 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A comparison of acute affective responses, physiological measures and training volume between superset and traditional resistance training in untrained adults.Front Sports Act Living. 2025 Jan 17;7:1536747. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2025.1536747. eCollection 2025. Front Sports Act Living. 2025. PMID: 39896990 Free PMC article.
-
EFFECT OF DIFFERENT FOAM ROLLING VOLUMES ON KNEE EXTENSION FATIGUE.Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2016 Dec;11(7):1076-1081. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2016. PMID: 27999722 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Simão R., de Salles B.F., Figueiredo T. Exercise order in resistance training. Sports Med. 2012;42:251–265. - PubMed
-
- Willardson J.M., Burkett L.N. The effect of rest interval length on the sustainability of squat and bench press repetitions. J Strength Cond Res. 2006;20:400–403. - PubMed
-
- de Salles B.F., Simão R., Miranda F. Rest interval between sets in strength training. Sports Med. 2009;39:765–777. - PubMed
-
- Miranda H., Simão R., dos Santos Vigário P. Exercise order interacts with rest interval during upper-body resistance exercise. J Strength Cond Res. 2010;24:1573–1577. - PubMed
-
- Folland J.P., Williams A.G. The adaptations to strength training: morphological and neurological contributions to increased strength. Sports Med. 2007;37:145–168. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

