MicroRNA-211 suppresses prostate cancer proliferation by targeting SPARC
- PMID: 29541199
- PMCID: PMC5835857
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.7877
MicroRNA-211 suppresses prostate cancer proliferation by targeting SPARC
Abstract
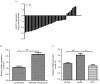
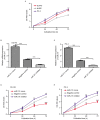
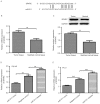
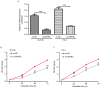
Dysregulation of microRNAs (miRNAs/miRs) is frequently associated with cancer progression. Altered expression of miR-211 has been observed in various types of human cancer; however, its expression and role in prostate cancer (PCa) remains unknown. In the present study, the expression of miR-211 in PCa cell lines and tissues was measured by reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (qPCR), revealing that miR-211 was downregulated in PCa cell lines and tissues. Further analysis revealed that low miR-211 was associated with the tumor stage and Gleason score. With the assistance of miR-211 mimics and inhibitor, it was also revealed that the overexpression of miR-211 could inhibit PCa cell proliferation in vitro. Conversely, downregulated miR-211 expression promotes PCa cell proliferation. In addition, the secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine (SPARC) was identified as a target of miR-211 in the PCa cell lines, and SPARC expression was inversely associated with miR-211. In conclusion, it was demonstrated that the miR-211 expression was downregulated in PCa cell lines and tissues. Additionally, miR-211 could inhibit PCa cell proliferation partially by downregulating SPARC. Therefore, miR-211 may be a potential therapeutic target for PCa treatment in the future.
Keywords: microRNA-211; proliferation; prostate cancer; secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-1291 mediates cell proliferation and tumorigenesis by downregulating MED1 in prostate cancer.Oncol Lett. 2019 Mar;17(3):3253-3260. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.9980. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 30867757 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-132/212 Upregulation Inhibits TGF-β-Mediated Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Prostate Cancer Cells by Targeting SOX4.Prostate. 2016 Dec;76(16):1560-1570. doi: 10.1002/pros.23241. Epub 2016 Aug 16. Prostate. 2016. PMID: 27527117
-
miR-211 inhibits proliferation, invasion and migration of cervical cancer via targeting SPARC.Oncol Lett. 2018 Jul;16(1):853-860. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8735. Epub 2018 May 17. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29963155 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-126 inhibits proliferation and metastasis in prostate cancer via regulation of ADAM9.Oncol Lett. 2018 Jun;15(6):9051-9060. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8528. Epub 2018 Apr 18. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29805636 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-425-5p promotes the development of prostate cancer via targeting forkhead box J3.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Jan;23(2):547-554. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201901_16867. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30720162
Cited by
-
Adaptive and non-adaptive gene expression responses in prostate cancer during androgen deprivation.PLoS One. 2023 Feb 21;18(2):e0281645. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281645. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36809527 Free PMC article.
-
The Paradoxical Behavior of microRNA-211 in Melanomas and Other Human Cancers.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 8;10:628367. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.628367. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33628737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-194 regulates cell viability and apoptosis by targeting CDH2 in prostatic cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Aug 14;11:4837-4844. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S169101. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 30147335 Free PMC article.
-
miR-129-5p inhibits prostate cancer proliferation via targeting ETV1.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 May 9;12:3531-3544. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S183435. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31190859 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-211-mediated targeting of the INHBA-TGF-β axis suppresses prostate tumor formation and growth.Cancer Gene Ther. 2021 May;28(5):514-528. doi: 10.1038/s41417-020-00237-w. Epub 2020 Nov 22. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021. Retraction in: Cancer Gene Ther. 2022 Jun;29(6):874. doi: 10.1038/s41417-022-00481-2. PMID: 33223523 Retracted.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
