Novel exostosin-2 mutation identified in a Chinese family with hereditary multiple osteochondroma
- PMID: 29541207
- PMCID: PMC5835906
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.7838
Novel exostosin-2 mutation identified in a Chinese family with hereditary multiple osteochondroma
Abstract
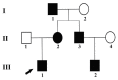
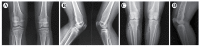
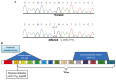
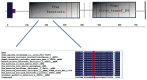
Hereditary multiple osteochondroma (HMO) is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder characterized by multiple outgrowing bony tumors capped by cartilage, generally affecting the metaphyses. The disease is known as hereditary multiple exostoses, familial exostosis, multiple cartilaginous exostoses or hereditary malformation of cartilage. The prevalence of HMO in Europe and the Unites States is ~1:100,000, although it has not been reported in China. The disease is often accompanied by pain, asymmetry and skeletal malformations, including forearm and leg bending deformities, limb length discrepancies, and knee internal and external rotation abnormalities. Mutations to exostosin-1 (EXT1) and EXT2 mutations cause insufficient heparan sulfate biosynthesis, leading to chondrocyte proliferation, abnormal bone growth in neighboring regions, multiple exostoses, and ultimately malignant transformation. The risk of malignant degeneration to osteochondrosarcoma increases with age, despite the low lifetime risk (~1%). The present study selected a clinical feature of typical HMO pedigrees, and examined mutations in family members by Sanger sequencing. Each of the five patients examined had a novel heterozygous nonsense mutation, c.67C>T p.Arg23*. The mutation is located prior to the EXT2 exostosin domains in the amino acid sequence and results in a protein truncation of the 705 C-terminal amino acids. The present study provides molecular genetic evidence for a novel causal mechanism of HMO, and provides the basis for clinical genetic counseling for similar diseases.
Keywords: exostosin-2; hereditary multiple osteochondroma; nonsense mutation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Novel EXT1 mutation identified in a pedigree with hereditary multiple exostoses.Oncol Rep. 2014 Feb;31(2):713-8. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2891. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Oncol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24297320
-
Identification of a novel frameshift mutation of the EXT2 gene in a family with multiple osteochondroma.Oncol Lett. 2016 Jan;11(1):105-110. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.3844. Epub 2015 Oct 29. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 26870176 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Novel Mutations in the EXT1 and EXT2 Genes of Chinese Patients with Hereditary Multiple Osteochondromas.Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2021 Feb;25(2):145-151. doi: 10.1089/gtmb.2020.0098. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2021. PMID: 33596140
-
Manifestations of hereditary multiple exostoses.J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2005 Mar-Apr;13(2):110-20. doi: 10.5435/00124635-200503000-00004. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2005. PMID: 15850368 Review.
-
Hereditary Multiple Exostoses: a review of clinical appearance and metabolic pattern.Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab. 2016 May-Aug;13(2):110-118. doi: 10.11138/ccmbm/2016.13.2.110. Epub 2016 Oct 5. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab. 2016. PMID: 27920806 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Arthroscopic Excision of an Intra-Articular Osteochondroma of the Knee.Cureus. 2021 Aug 13;13(8):e17154. doi: 10.7759/cureus.17154. eCollection 2021 Aug. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34532184 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical survey of a pedigree with hereditary multiple exostoses and identification of EXT‑2 gene deletion mutation.Mol Med Rep. 2022 Apr;25(4):141. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12657. Epub 2022 Feb 25. Mol Med Rep. 2022. PMID: 35211766 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Effect of Arthroscopic Resection of Extra-Articular Knee Osteochondroma.J Clin Med. 2022 Dec 21;12(1):52. doi: 10.3390/jcm12010052. J Clin Med. 2022. Retraction in: J Clin Med. 2023 Sep 05;12(18):5778. doi: 10.3390/jcm12185778. PMID: 36614849 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Arthroscopic resection of extra-articular knee osteochondroma: report of two cases.J Surg Case Rep. 2019 Jun 14;2019(6):rjz167. doi: 10.1093/jscr/rjz167. eCollection 2019 Jun. J Surg Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31214309 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
