Necrotizing Fasciitis of Thoracic and Abdominal Wall with Emphysematous Pyelonephritis and Retroperitoneal Abscess
- PMID: 29541493
- PMCID: PMC5843965
- DOI: 10.4103/jcis.JCIS_56_17
Necrotizing Fasciitis of Thoracic and Abdominal Wall with Emphysematous Pyelonephritis and Retroperitoneal Abscess
Abstract
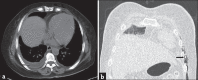
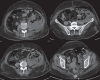
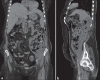
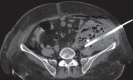
Emphysematous pyelonephritis is a life-threatening severe form of pyelonephritis usually occurring in patients with diabetes mellitus with or without obstructive uropathies in whom there is necrotizing infection leading to the gas production of an unclear mechanism involving the renal parenchyma and the collecting system. Necrotizing fasciitis is characterized by progressive necrosis of fat and fascia due to deep-seated infection of subcutaneous tissue. It has a fulminant course with considerable mortality. Diabetes Mellitus is a common predisposing factor. The combined occurrence of emphysematous pyelonephritis and necrotizing fasciitis is extremely unusual. Early recognition and management is mandatory to avoid mortality. We report a case of a 53-year-old female, a known case of Type II diabetes mellitus, who presented with necrotizing fasciitis of thoracic and abdominal wall with emphysematous pyelonephritis in the left kidney with a retroperitoneal abscess.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; emphysematous pyelonephritis; lumbar triangle; necrotizing fasciitis; retroperitoneal abscess.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ye YX, Wen YK. Emphysematous pyelonephritis presenting as necrotizing fasciitis of the leg. J Chin Med Assoc. 2009;72:160–2. - PubMed
-
- Wan YL, Lo SK, Bullard MJ, Chang PL, Lee TY. Predictors of outcome in emphysematous pyelonephritis. J Urol. 1998;159:369–73. - PubMed
-
- Best CD, Terris MK, Tacker JR, Reese JH. Clinical and radiological findings in patients with gas forming renal abscess treated conservatively. J Urol. 1999;162:1273–6. - PubMed
-
- Chan PH, Kho VK, Lai SK, Yang CH, Chang HC, Chiu B, et al. Treatment of emphysematous pyelonephritis with broad-spectrum antibacterials and percutaneous renal drainage: An analysis of 10 patients. J Chin Med Assoc. 2005;68:29–32. - PubMed
-
- Daly JJ, Jr, Alderman DF, Conway WF. General case of the day. Radio Graph. 1995;15:489–92. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

