Left atrial function: evaluation by strain analysis
- PMID: 29541609
- PMCID: PMC5835645
- DOI: 10.21037/cdt.2017.06.08
Left atrial function: evaluation by strain analysis
Abstract
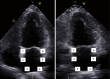
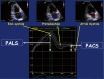
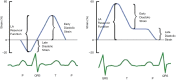
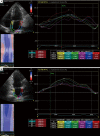
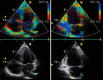
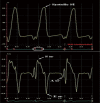
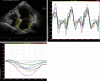
The left atrium has an important role in modulating left ventricular filling and is an important biomarker of cardiovascular disease and adverse cardiovascular outcomes. While previously left atrial (LA) size was utilised, the role of LA function as a biomarker is increasingly being evaluated, both independently and also in combination with LA size. Strain analysis has been utilised for evaluation of LA function and can be measured throughout the cardiac cycle, thereby enabling the evaluation of LA reservoir, conduit and contractile function. Strain evaluates myocardial deformation while strain rate examines the rate of change in strain. This review will focus on the various types of strain analysis for evaluation of LA function, alterations in LA strain in physiological and pathologic states that alter LA function and finally evaluate its utility as a prognostic marker.
Keywords: LA longitudinal strain; Left atrial strain (LA strain); left atrial function (LA function); strain echocardiography.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
