Echocardiographic feature of diabetic cardiomyopathy: where are we now?
- PMID: 29541610
- PMCID: PMC5835643
- DOI: 10.21037/cdt.2018.01.03
Echocardiographic feature of diabetic cardiomyopathy: where are we now?
Abstract
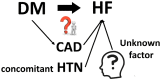
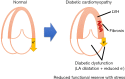
We are now entering the very exciting era of treatment and management of diabetes mellitus (DM) with the emergence of new therapeutic agents, including sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor (DPP-4i). From a cardiology and echocardiography perspective, the existence of diabetic cardiomyopathy has been proven through over four decades of discussion. DM is highly prevalent in patients with heart failure (HF). Independent associations are found after adjusting for hypertension (HTN) and coronary artery disease (CAD). In patients with both DM and HF, the prognosis is extremely dismal. In this review, the main focus is on both diabetic cardiomyopathy per se and its typical features (including myocardial additive insult related to DM), diagnosis, and management.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus (DM); diabetic cardiomyopathy; echocardiography; myocardial strain; sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The author has no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diabetes Mellitus and Heart Failure.J Clin Med. 2021 Aug 19;10(16):3682. doi: 10.3390/jcm10163682. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34441977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination Therapy with a Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor and a Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Additively Suppresses Macrophage Foam Cell Formation and Atherosclerosis in Diabetic Mice.Int J Endocrinol. 2017;2017:1365209. doi: 10.1155/2017/1365209. Epub 2017 Mar 19. Int J Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28408925 Free PMC article.
-
Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Risk of Heart Failure in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Population-Based Cohort Study.Circ Heart Fail. 2017 Sep;10(9):e003957. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.117.003957. Circ Heart Fail. 2017. PMID: 28899989
-
Cardiovascular effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in diabetic patients: A meta-analysis.Int J Cardiol. 2015 Feb 15;181:239-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.12.017. Epub 2014 Dec 3. Int J Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25528528
-
Heart failure in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: assessment with echocardiography and effects of antihyperglycemic treatments.J Echocardiogr. 2019 Dec;17(4):177-186. doi: 10.1007/s12574-019-00446-9. Epub 2019 Oct 15. J Echocardiogr. 2019. PMID: 31617144 Review.
Cited by
-
Early Identification and Management of Heart Failure in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus in the United Arab Emirates: A Call to Action.J Saudi Heart Assoc. 2023 Aug 5;35(2):192-199. doi: 10.37616/2212-5043.1342. eCollection 2023. J Saudi Heart Assoc. 2023. PMID: 38318530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Basic Mechanisms of Diabetic Heart Disease.Circ Res. 2020 May 22;126(11):1501-1525. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.315913. Epub 2020 May 21. Circ Res. 2020. PMID: 32437308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Echocardiography, an Indispensable Tool for the Management of Diabetics, with or without Coronary Artery Disease, in Clinical Practice.Medicina (Kaunas). 2020 Dec 18;56(12):709. doi: 10.3390/medicina56120709. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020. PMID: 33352952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Echocardiographic Changes in Saudi Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Nov 10;59(11):1985. doi: 10.3390/medicina59111985. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 38004034 Free PMC article.
-
Sacubitril/Valsartan Combination Partially Improves Cardiac Systolic, but Not Diastolic, Function through β-AR Responsiveness in a Rat Model of Type 2 Diabetes.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 2;25(19):10617. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910617. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408945 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
