Neutrosophic segmentation of breast lesions for dedicated breast computed tomography
- PMID: 29541650
- PMCID: PMC5839418
- DOI: 10.1117/1.JMI.5.1.014505
Neutrosophic segmentation of breast lesions for dedicated breast computed tomography
Abstract
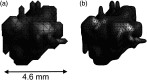
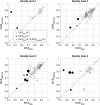
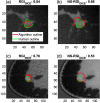
We proposed the neutrosophic approach for segmenting breast lesions in breast computed tomography (bCT) images. The neutrosophic set considers the nature and properties of neutrality (or indeterminacy). We considered the image noise as an indeterminate component while treating the breast lesion and other breast areas as true and false components. We iteratively smoothed and contrast-enhanced the image to reduce the noise level of the true set. We then applied one existing algorithm for bCT images, the RGI segmentation, on the resulting noise-reduced image to segment the breast lesions. We compared the segmentation performance of the proposed method (named as NS-RGI) to that of the regular RGI segmentation. We used 122 breast lesions (44 benign and 78 malignant) of 111 noncontrast enhanced bCT cases. We measured the segmentation performances of the NS-RGI and the RGI using the Dice coefficient. The average Dice values of the NS-RGI and RGI were 0.82 and 0.80, respectively, and their difference was statistically significant ([Formula: see text]). We conducted a subsequent feature analysis on the resulting segmentations. The classifier performance for the NS-RGI ([Formula: see text]) improved over that of the RGI ([Formula: see text], [Formula: see text]).
Keywords: CADx; breast CT; neutrosophy; quantitative feature analysis; segmentation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Transfer learning for automatic joint segmentation of thyroid and breast lesions from ultrasound images.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2022 Feb;17(2):363-372. doi: 10.1007/s11548-021-02505-y. Epub 2021 Dec 8. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2022. PMID: 34881409
-
Segmentation of breast masses on dedicated breast computed tomography and three-dimensional breast ultrasound images.J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2014 Apr;1(1):014501. doi: 10.1117/1.JMI.1.1.014501. Epub 2014 Apr 23. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2014. PMID: 32855995 Free PMC article.
-
Level set segmentation of breast masses in contrast-enhanced dedicated breast CT and evaluation of stopping criteria.J Digit Imaging. 2014 Apr;27(2):237-47. doi: 10.1007/s10278-013-9652-1. J Digit Imaging. 2014. PMID: 24162667 Free PMC article.
-
NeDSeM: Neutrosophy Domain-Based Segmentation Method for Malignant Melanoma Images.Entropy (Basel). 2022 Jun 2;24(6):783. doi: 10.3390/e24060783. Entropy (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35741504 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal reconstruction and quantitative image features for computer-aided diagnosis tools for breast CT.Med Phys. 2017 May;44(5):1846-1856. doi: 10.1002/mp.12214. Epub 2017 Apr 13. Med Phys. 2017. PMID: 28295405 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Relationship between computer segmentation performance and computer classification performance in breast CT: A simulation study using RGI segmentation and LDA classification.Med Phys. 2018 Jun 19:10.1002/mp.13054. doi: 10.1002/mp.13054. Online ahead of print. Med Phys. 2018. PMID: 29920684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antropova N., et al. , “Efficient iterative image reconstruction algorithm for dedicated breast CT,” Proc. SPIE 9783, 97834K (2016).CHETBFhttps://doi.org/10.1117/12.2216933PSISDG - DOI
-
- Sidky E. Y., Pan X., “Image reconstruction in circular cone-beam computed tomography by constrained, total-variation minimization,” Phys. Med. Biol. 53(17), 4777–4807 (2008).PHMBA7https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/53/17/021 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Smarandache F., Unifying A, Field in Logics: Neutrosophic Logic. Neutrosophy, Neutrosophic Set, Neutrosophic Probability, American Research Press, Rehoboth, New Mexico: (2003).
-
- Zhang M., Zhang L., Cheng H. D., “A neutrosophic approach to image segmentation based on watershed method,” Signal Process. 90(5), 1510–1517 (2010).https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2009.10.021 - DOI
-
- Guo Y., Cheng H. D., “New neutrosophic approach to image segmentation,” Pattern Recogn. 42(5), 587–595 (2009).https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2008.10.002 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

