Identification of serotonin 2A receptor as a novel HCV entry factor by a chemical biology strategy
- PMID: 29542010
- PMCID: PMC6338621
- DOI: 10.1007/s13238-018-0521-z
Identification of serotonin 2A receptor as a novel HCV entry factor by a chemical biology strategy
Abstract
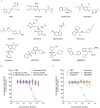
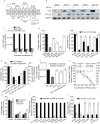
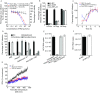
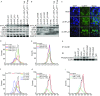
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a leading cause of liver disease worldwide. Although several HCV protease/polymerase inhibitors were recently approved by U.S. FDA, the combination of antivirals targeting multiple processes of HCV lifecycle would optimize anti-HCV therapy and against potential drug-resistance. Viral entry is an essential target step for antiviral development, but FDA-approved HCV entry inhibitor remains exclusive. Here we identify serotonin 2A receptor (5-HT2AR) is a HCV entry factor amendable to therapeutic intervention by a chemical biology strategy. The silencing of 5-HT2AR and clinically available 5-HT2AR antagonist suppress cell culture-derived HCV (HCVcc) in different liver cells and primary human hepatocytes at late endocytosis process. The mechanism is related to regulate the correct plasma membrane localization of claudin 1 (CLDN1). Moreover, phenoxybenzamine (PBZ), an FDA-approved 5-HT2AR antagonist, inhibits all major HCV genotypes in vitro and displays synergy in combination with clinical used anti-HCV drugs. The impact of PBZ on HCV genotype 2a is documented in immune-competent humanized transgenic mice. Our results not only expand the understanding of HCV entry, but also present a promising target for the invention of HCV entry inhibitor.
Keywords: HCV; antiviral drug; entry; serotonin 2A receptor.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of Piperazinylbenzenesulfonamides as New Inhibitors of Claudin-1 Trafficking and Hepatitis C Virus Entry.J Virol. 2018 Apr 27;92(10):e01982-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01982-17. Print 2018 May 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29491159 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 cholesterol absorption receptor as a new hepatitis C virus entry factor.Nat Med. 2012 Jan 8;18(2):281-5. doi: 10.1038/nm.2581. Nat Med. 2012. PMID: 22231557 Free PMC article.
-
Monoclonal antibodies against extracellular domains of claudin-1 block hepatitis C virus infection in a mouse model.J Virol. 2015 May;89(9):4866-79. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03676-14. Epub 2015 Feb 11. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25673725 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C virus entry into hepatocytes: molecular mechanisms and targets for antiviral therapies.J Hepatol. 2011 Mar;54(3):566-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.10.014. Epub 2010 Nov 11. J Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21146244 Review.
-
Entry inhibitors: New advances in HCV treatment.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2016 Jan 6;5(1):e3. doi: 10.1038/emi.2016.3. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2016. PMID: 26733381 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatitis C Virus Entry: An Intriguingly Complex and Highly Regulated Process.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 18;21(6):2091. doi: 10.3390/ijms21062091. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32197477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Serotonin in Concanavalin A-Induced Liver Injury in Mice.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Jan 6;2020:7504521. doi: 10.1155/2020/7504521. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 31998441 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonergic Drugs Inhibit Chikungunya Virus Infection at Different Stages of the Cell Entry Pathway.J Virol. 2020 Jun 16;94(13):e00274-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00274-20. Print 2020 Jun 16. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32321803 Free PMC article.
-
The janus face of serotonin: Regenerative promoter and chronic liver disease aggravator.Heliyon. 2024 May 3;10(9):e30703. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30703. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38756588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Role of l-Dopa Decarboxylase in Flaviviridae Virus Infections.Cells. 2019 Aug 5;8(8):837. doi: 10.3390/cells8080837. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31387309 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnes NM, Sharp T 91999) A review of central 5-HT receptors and their function. Neuropharmacology 38(8):1083–1152 (Epub 16 Aug 1999) - PubMed
-
- Berg KA, Clarke WP, Chen Y, Ebersole BJ, McKay RD, Maayani S. 5-Hydroxytryptamine type 2A receptors regulate cyclic AMP accumulation in a neuronal cell line by protein kinase C-dependent and calcium/calmodulin-dependent mechanisms. Mol Pharmacol. 1994;45(5):826–836. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

